SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2: The biology and clinical data settling the ARB and ACEI controversy
- PMID: 32771682
- PMCID: PMC7415847
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102907
SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2: The biology and clinical data settling the ARB and ACEI controversy
Abstract
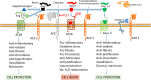
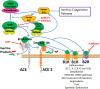
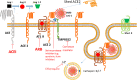
Background: SARS-CoV-2 enters cells by binding of its spike protein to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) have been reported to increase ACE2 expression in animal models, and worse outcomes are reported in patients with co-morbidities commonly treated with these agents, leading to controversy during the COVID-19 pandemic over whether these drugs might be helpful or harmful.
Methods: Animal, in vitro and clinical data relevant to the biology of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), its interaction with the kallikrein-kinin system (KKS) and SARS-CoV-2, and clinical studies were reviewed.
Findings and interpretation: SARS-CoV-2 hijacks ACE2to invade and damage cells, downregulating ACE2, reducing its protective effects and exacerbating injurious Ang II effects. However, retrospective observational studies do not show higher risk of infection with ACEI or ARB use. Nevertheless, study of the RAS and KKS in the setting of coronaviral infection may yield therapeutic targets.
Keywords: ACE inhibitors; ACE2; ARBs; COVID-19; Kallikrein-kinin system; Renin-angiotensin system; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ferrario C.M., Jessup J., Chappell M.C., Averill D.B., Brosnihan K.B., Tallant E.A. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Circulation. 2005;111(20):2605–2610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

