An insight on medicinal attributes of 1,2,4-triazoles
- PMID: 32771798
- PMCID: PMC7384432
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112652
An insight on medicinal attributes of 1,2,4-triazoles
Abstract
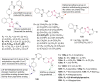
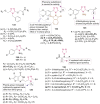
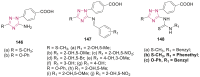
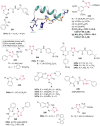
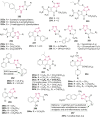
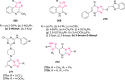
The present review aims to summarize the pharmacological profile of 1,2,4-triazole, one of the emerging privileged scaffold, as antifungal, antibacterial, anticancer, anticonvulsant, antituberculosis, antiviral, antiparasitic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents, etc. along with structure-activity relationship. The comprehensive compilation of work carried out in the last decade on 1,2,4-triazole nucleus will provide inevitable scope for researchers for the advancement of novel potential drug candidates having better efficacy and selectivity.
Keywords: 1,2,4-Triazole; Enzyme inhibitors; Hybrid compounds; Molecular interactions; Pharmacological activities; Structure-activity relationship.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


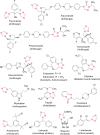
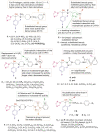


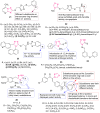

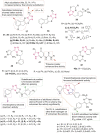

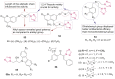



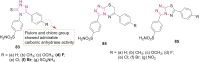
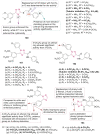
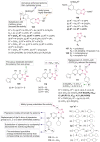
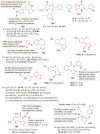
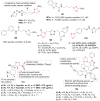
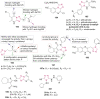
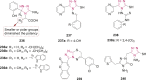
 O group and Lys868.
O group and Lys868.














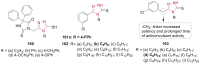







References
-
- Fan Y.L., Ke X., Liu M. Coumarin-triazole hybrids and their biological activities. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2018;55:791–802.
-
- Cox J.R., Woodcock S., Hillier I.H., Vincent M.A. Tautomerism of 1,2,3- and 1,2,4-triazole in the gas phase and in aqueous solution: a combined ab Initio quantum mechanics and free energy perturbation study. J. Phys. Chem. 1990;94:5499–5501.
-
- Peyton L.R., Gallagher S., Hashemzadeh M. Triazole antifungals: a review. Drugs Today. 2015;51:705–718. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C.-H., Wang Y. Recent researches in triazole compounds as medicinal drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012;19:239–280. - PubMed
-
- Russell P.E. A century of fungicide evolution. J. Agric. Sci. 2005;143:11–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

