ALKBH5 suppresses malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-guided epigenetic inhibition of LYPD1
- PMID: 32772918
- PMCID: PMC7416417
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01239-w
ALKBH5 suppresses malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-guided epigenetic inhibition of LYPD1
Abstract
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is an emerging layer of epigenetic regulation which is widely implicated in the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), offering a novel perspective for investigating molecular pathogenesis of this disease. The role of AlkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5), one of the m6A demethylases, has not been fully explored in HCC. Here we clarify the biological profile and potential mechanisms of ALKBH5 in HCC.
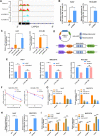
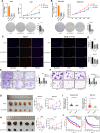
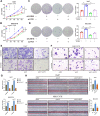
Methods: Expression of ALKBH5 and its correlation with clinicopathological characteristics of HCC were evaluated using tissue microarrays and online datasets. And biological effects of ALKBH5 in HCC were determined in vitro and in vivo. Subsequently, methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq) combined with RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), and following m6A dot blot, MeRIP-qPCR, RIP-qPCR or dual luciferase reporter assays were employed to screen and validate the candidate targets of ALKBH5.
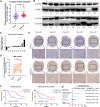
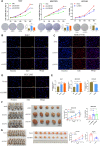
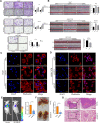
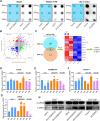
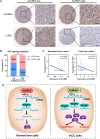
Results: We demonstrated that ALKBH5 was down-regulated in HCC, and decreased ALKBH5 expression was an independent prognostic factor of worse survival in HCC patients. Functionally, ALKBH5 suppressed the proliferation and invasion capabilities of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation led to a post-transcriptional inhibition of LY6/PLAUR Domain Containing 1 (LYPD1), which could be recognized and stabilized by the m6A effector IGF2BP1. In addition, we identified that LYPD1 induced oncogenic behaviors of tumors in contrast to ALKBH5. Dysregulation of ALKBH5/LYPD1 axis impelled the progression of HCC.
Conclusion: Our study reveals that ALKBH5, characterized as a tumor suppressor, attenuates the expression of LYPD1 via an m6A-dependent manner in HCC cells. Our findings enrich the landscape of m6A-modulated tumor malignancy, and provide new insights into potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets of HCC treatment.
Keywords: ALKBH5; Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); LYPD1; N6-methyladenosine (m6A).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Yegin EG, Oymaci E, Karatay E, Coker A. Progress in surgical and nonsurgical approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2016;15:234–256. - PubMed
-
- Rebouissou S, Nault JC. Advances in molecular classification and precision oncology in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2020;72:215–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

