The autophagy adaptor NDP52 and the FIP200 coiled-coil allosterically activate ULK1 complex membrane recruitment
- PMID: 32773036
- PMCID: PMC7447430
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.59099
The autophagy adaptor NDP52 and the FIP200 coiled-coil allosterically activate ULK1 complex membrane recruitment
Abstract
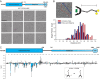
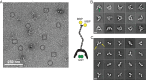
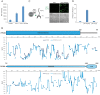
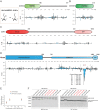
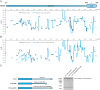
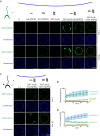
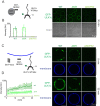
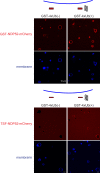
The selective autophagy pathways of xenophagy and mitophagy are initiated when the adaptor NDP52 recruits the ULK1 complex to autophagic cargo. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange coupled to mass spectrometry (HDX-MS) was used to map the membrane and NDP52 binding sites of the ULK1 complex to unique regions of the coiled coil of the FIP200 subunit. Electron microscopy of the full-length ULK1 complex shows that the FIP200 coiled coil projects away from the crescent-shaped FIP200 N-terminal domain dimer. NDP52 allosterically stimulates membrane-binding by FIP200 and the ULK1 complex by promoting a more dynamic conformation of the membrane-binding portion of the FIP200 coiled coil. Giant unilamellar vesicle (GUV) reconstitution confirmed that membrane recruitment by the ULK1 complex is triggered by NDP52 engagement. These data reveal how the allosteric linkage between NDP52 and the ULK1 complex could drive the first membrane recruitment event of phagophore biogenesis in xenophagy and mitophagy.
Keywords: HDX-MS; autophagy; biochemistry; cell biology; chemical biology; coiled-coil; electron microscopy; human; mitophagy; xenophagy.
© 2020, Shi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
XS, CC, AY, LJ No competing interests declared, JH JHH is co-founder of Casma Therapeutics
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

