Identification of COVID-19 samples from chest X-Ray images using deep learning: A comparison of transfer learning approaches
- PMID: 32773400
- PMCID: PMC7592691
- DOI: 10.3233/XST-200715
Identification of COVID-19 samples from chest X-Ray images using deep learning: A comparison of transfer learning approaches
Abstract
Background: The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) constitutes a public health emergency globally. The number of infected people and deaths are proliferating every day, which is putting tremendous pressure on our social and healthcare system. Rapid detection of COVID-19 cases is a significant step to fight against this virus as well as release pressure off the healthcare system.
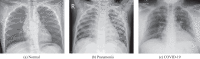
Objective: One of the critical factors behind the rapid spread of COVID-19 pandemic is a lengthy clinical testing time. The imaging tool, such as Chest X-ray (CXR), can speed up the identification process. Therefore, our objective is to develop an automated CAD system for the detection of COVID-19 samples from healthy and pneumonia cases using CXR images.
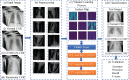
Methods: Due to the scarcity of the COVID-19 benchmark dataset, we have employed deep transfer learning techniques, where we examined 15 different pre-trained CNN models to find the most suitable one for this task.
Results: A total of 860 images (260 COVID-19 cases, 300 healthy and 300 pneumonia cases) have been employed to investigate the performance of the proposed algorithm, where 70% images of each class are accepted for training, 15% is used for validation, and rest is for testing. It is observed that the VGG19 obtains the highest classification accuracy of 89.3% with an average precision, recall, and F1 score of 0.90, 0.89, 0.90, respectively.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the effectiveness of deep transfer learning techniques for the identification of COVID-19 cases using CXR images.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest X-Ray Image; image identification; transfer learning.
Figures



References
-
- Novel Coronavirus – China, World Health Organization, (2020). https://www.who.int/csr/don/12-january-2020-novel-coronavirus-china/en/.
-
- Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations Emergency Committee regarding the out of novel coronavirus -nCoV), World Health Organization, (2019). https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-....
-
- WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March World Health Organization, (2020). https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....
-
- JHU, COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU), (2020). https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- Zhao S., Lin Q., Ran J., Musa S.S., Yang G., Wang W., Lou Y., Gao D., Yang L., He D., et al. , Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus -nCoV) in China, from to: A data-driven analysis in the early phase of the out, International Journal of Infectious Diseases 92 (2020), 214–217. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

