[Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in renal transplant recipients: A case report]
- PMID: 32773818
- PMCID: PMC7433616
- DOI: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.033
[Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in renal transplant recipients: A case report]
Abstract
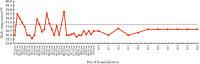
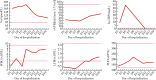
The novel coronavirus is a newly discovered pathogen in late December 2019, and its source is currently unknown, which can lead to asymptomatic infection, new coronavirus pneumonia or serious complications, such as acute respiratory failure. Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a new type of respiratory disease that is currently spreading all over the world and caused by this coronavirus. Its common symptoms are highly similar to those of other viruses, such as fever, cough and dyspnea. There is currently no vaccine or treatment for COVID-19. Everyone is susceptible to infection with this disease, and owing to the long-term use of immunosuppressants, the immunity of kidney transplant recipients is suppressed, and it is more likely to be infected with the disease. At present, its impact on kidney transplant recipients is unclear. This article reports the clinical features and therapeutic course of novel coronavirus infection in a patient after renal transplantation. A 37-year-old female patient who received a kidney transplant 6 months before was diagnosed with novel coronavirus pneumonia. The patient's symptoms (such as fever, chills, dry cough, muscle aches), laboratory tests (such as decreased white blood cell count, elevated liver enzymes and D-dimer, positive viral nucleic acid test), and chest CT (multiple left lower lung plaque ground glass shadow) were similar to those of non-transplanted novel coronavirus pneumonia patients. In terms of treatment, because the immunity of kidney transplant recipients has been suppressed for a long time, it is a very common strategy to suspend the use of immunosuppressive agents. Therefore, the patient immediately discontinued the immunosuppressive agent after admission, so that she could restore immunity against infection in a short time. At the same time, the use of glucocorticoids was also very important. Its immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects played a large role in the treatment process.In addition, prophylactic antibiotics was needed, and nephrotoxic drugs should be used with caution. Finally, following discounting the use of immunosuppressant and a low-dose glucocorticoid-based treatment regimen, COVID-19 in this renal transplant recipient was successfully cured. The cure of this case was of great significance, and this adjuvant nonspecific antiviral therapy could provide a template for the treatment of other such patients.
Keywords: Corona virus disease 2019; Immunosuppressive agents; Kidney transplantation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Immunosuppressed Renal Transplant Recipients: A Summary of 10 Confirmed Cases in Wuhan, China.Eur Urol. 2020 Jun;77(6):748-754. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.039. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Eur Urol. 2020. PMID: 32317180 Free PMC article.
-
Novel coronavirus infection and acute kidney injury in two renal transplant recipients: a case report.J Int Med Res. 2020 Oct;48(10):300060520964009. doi: 10.1177/0300060520964009. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 33100064 Free PMC article.
-
Different clinical presentations of two renal transplant recipients with coronavirus disease 2019: a case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Sep 25;20(1):707. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05434-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32977764 Free PMC article.
-
Covid-19 in kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review of the case series available three months into the pandemic.Infect Dis (Lond). 2020 Nov;52(11):830-837. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2020.1792977. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Infect Dis (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32657186
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Immunocompromised Organ Transplant Recipients: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Transplant Proc. 2020 Nov;52(9):2698-2702. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.07.014. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Transplant Proc. 2020. PMID: 32800516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current literature.Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2021 Jan;35(1):100588. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2020.100588. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2021. PMID: 33246166 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients [J]. Am J Transplant, 2009, 9(Suppl 3): S1-155. 10.1038/ki.2009.377
-
-
- Zhang H, Chen Y, Yuan Q, et al. Identification of kidney transplant recipients with coronavirus disease 2019. https://www.europeanurology.com/article/S0302-2838(20)30205-0/abstract. Eur Urol. 2020;77(6):742–747. - PMC - PubMed
