Cynanchum paniculatum and Its Major Active Constituents for Inflammatory-Related Diseases: A Review of Traditional Use, Multiple Pathway Modulations, and Clinical Applications
- PMID: 32774428
- PMCID: PMC7396087
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7259686
Cynanchum paniculatum and Its Major Active Constituents for Inflammatory-Related Diseases: A Review of Traditional Use, Multiple Pathway Modulations, and Clinical Applications
Abstract
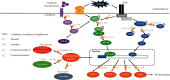
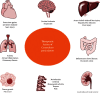
Cynanchum paniculatum Radix, known as Xuchangqing in Chinese, is commonly prescribed in Chinese Medicine (CM) for the treatment of various inflammatory diseases. The anti-inflammatory property of Cynanchum paniculatum can be traced from its wind-damp removing, collaterals' obstruction relieving, and toxins counteracting effects as folk medicine in CM. This paper systematically reviewed the research advancement of the pharmacological effects of Cynanchum paniculatum among a variety of human diseases, including diseases of the respiratory, circulatory, digestive, urogenital, hematopoietic, endocrine and metabolomic, neurological, skeletal, and rheumatological systems and malignant diseases. This review aims to link the long history of clinical applications of Cynanchum paniculatum in CM with recent biomedical investigations. The major bioactive chemical compositions of Cynanchum paniculatum and their associated action mechanism unveiled by biomedical investigations as well as the present clinical applications and future perspectives are discussed. The major focuses of this review are on the diverse mechanisms of Cynanchum paniculatum and the role of its active components in inflammatory diseases.
Copyright © 2020 Jing-xian Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cynanchum paniculatum (Bunge) Kitag. ex H. Hara: A review of its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;260:112994. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112994. Epub 2020 May 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32473366
-
Network Pharmacological Study on the Mechanism of Cynanchum paniculatum (Xuchangqing) in the Treatment of Bungarus multicinctus Bites.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 5;2022:3887072. doi: 10.1155/2022/3887072. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35837378 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Deinagkistrodon acutus venom properties of ethanolic root extract from Cynanchum paniculatum (Bunge) kitag and its GC-MS analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Oct 28;225:189-197. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30033377
-
Comparison of the Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Xiaoyuningkun Decoction with Cynanchum Paniculatum and Fukeqianjin in a Mouse Model of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Nov 30;25:9094-9102. doi: 10.12659/MSM.916070. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31784502 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese endemic medicinal plant Bolbostemma paniculatum (Maxim.) Franquet: A comprehensive review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 7;13:974054. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.974054. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160391 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Water Extract of Cynanchum paniculatum (Bge.) Kitag. on Different Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 May 19;2021:6665949. doi: 10.1155/2021/6665949. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34122605 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Cynanchum acutum L. Isolated Flavonoids Using Experimentally Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Biological and In Silico Investigation for NF-κB Pathway/miR-146a Expression Modulation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 27;10(11):1713. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111713. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829584 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolome combined with gut microbiome revealed the lipid-lowering mechanism of Xuezhiping capsule on hyperlipidemic hamster induced by high fat diet.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 20;10:1147910. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1147910. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36891237 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation indicators of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes for gouty arthritis with damp heat accumulation and the effect of administering Tongfeng Qingxiao formula.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Dec;44(6):1204-1216. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240706.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39617706 Free PMC article.
-
Cynanchum paniculatum (Bunge) Kitag. ex H.Hara inhibits pancreatic cancer progression by inducing caspase-dependent apoptosis and suppressing TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 31;15:1284371. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1284371. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38881872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun X. S. Fengyi, Shen Nong’s Herbal Classic. Beijing, China: People’s Health Press; 1982.
-
- Chen Y. X., Jiang S. P. Advances and application in the studies of the Pycnostelma paniculatum (Bunge) K. S. and paeonol. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 2007;19:311–314. - PubMed
-
- Mitsuhashi H., Hayashi K., Nomura T. Studies on the constituents of asclepiadaceae plants. 8. Components of Cynanchum paniculatum Kitagawa. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 1966;14(7):779–783. - PubMed
-
- Sugama K., Hayashi K., Mitsuhashi H., Kaneko K. Studies on the constituents of Asclepiadaceae plants. LXVI. The structures of three new glycosides, cynapanosides A, B, and C, from the Chinese drug “xu-chang-qing,” Cynanchum paniculatum Kitagawa. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 1988;34(11):4500–4507. doi: 10.1248/cpb.34.4500. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

