Traditional Chinese medicine for anti-Alzheimer's disease: berberine and evodiamine from Evodia rutaecarpa
- PMID: 32774447
- PMCID: PMC7409421
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-020-00359-1
Traditional Chinese medicine for anti-Alzheimer's disease: berberine and evodiamine from Evodia rutaecarpa
Abstract
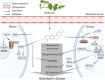
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common diseases in elderly people with a high incidence of dementia at approximately 60-80%. The pathogenesis of AD was quite complicated and currently there is no unified conclusion in the academic community, so no efficiently clinical treatment is available. In recent years, with the development of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), researchers have proposed the idea of relying on TCM to prevent and treat AD based on the characteristic of multiple targets of TCM. This study reviewed the pathological hypothesis of AD and the potential biomarkers found in the current researches. And the potential targets of berberine and evodiamine from Evodia rutaecarpa in AD were summarized and further analyzed. A compound-targets-pathway network was carried out to clarify the mechanism of action of berberine and evodiamine for AD. Furthermore, the limitations of current researches on the TCM and AD were discussed. It is hoped that this review will provide some references for development of TCM in the prevention and treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Berberine; Evodiamine; Pathogenic hypothesis; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

