Increased Serum Level and High Tissue Immunoexpression of Interleukin 17 in Cutaneous Lichen Planus: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Recalcitrant Cases?
- PMID: 32774513
- PMCID: PMC7396028
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6521274
Increased Serum Level and High Tissue Immunoexpression of Interleukin 17 in Cutaneous Lichen Planus: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Recalcitrant Cases?
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-17 is supposed to play an important role in the pathogenesis of oral lichen planus (OLP). However, there is scarce data in the literature on its significance in the cutaneous variant of the disease.
Objectives: To determine the serum level and tissue immunoexpression of IL-17 in cutaneous lichen planus (CLP).
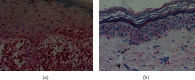
Methods: Fifty-two adult patients with CLP, without any significant autoimmune or inflammatory conditions, were included in the first part of the study. The control group consisted of 27 age- and sex-matched healthy volunteers. Serum concentration of IL-17 was quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit. In the second part of the study, the tissue expression of IL-17 was assessed in archival paraffin-embedded biopsy specimens from CLP (n = 14) against normal control tissues (n = 11) using immunohistochemical assays. The expression was evaluated using Zeiss Axio Imager A2 light microscope. Positively stained cells were counted in 10 fields of view for biopsy specimen at 200x magnification, and the mean value was calculated.
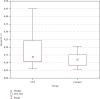
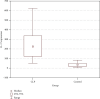
Results: The serum level of IL-17 was significantly elevated in patients with CLP, compared with healthy volunteers (0.218 ± 0.221 ng/ml versus 0.126 ± 0.058 ng/ml, respectively; p = 0.025). No correlation was found between the serum concentration of IL-17 and patient age, gender, disease duration, extent of skin involvement, the presence or intensity of pruritus, and coexistence of mucosal lesions. In tissue samples from CLP lesions, significantly higher numbers of cells expressing IL-17 were found when compared to a healthy skin (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Elevated serum concentration of IL-17 and high expression in a lesional skin support the hypothesis that IL-17 is implicated in the immunopathogenesis of CLP. These findings may constitute a premise for the future use of anti-IL-17 monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of severe and recalcitrant forms of CLP.
Copyright © 2020 Magdalena Żychowska et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of correlation between transcription factors and IL-17 in oral and cutaneous lichen planus lesions and Leukocytes.Cytokine. 2021 Dec;148:155696. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155696. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 34509039
-
Assessment of interleukin-18 gene polymorphism and serum levels in cutaneous lichen planus.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jun 26;29(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01846-z. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38918874 Free PMC article.
-
The inflammation in cutaneous lichen planus is dominated by IFN-ϒ and IL-21-A basis for therapeutic JAK1 inhibition.Exp Dermatol. 2021 Feb;30(2):262-270. doi: 10.1111/exd.14226. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Exp Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33113249
-
Childhood lichen planus pemphigoides: a case report and review of the literature.Pediatr Dermatol. 2009 Sep-Oct;26(5):569-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2009.00988.x. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19840313 Review.
-
The challenges of managing refractory oesphageal lichen planus.Ir J Med Sci. 2015 Mar;184(1):75-6. doi: 10.1007/s11845-014-1136-x. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Ir J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 24913736 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Insight into Lichen Planus Immunopathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 3;24(3):3038. doi: 10.3390/ijms24033038. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin-infiltrating T cells display distinct inflammatory signatures in lichen planus, bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 20;14:1203776. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1203776. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37415985 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Serum Interleukin-23 Levels in Patients with Oral and Cutaneous Lichen Planus.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Jul 12;2021:5578568. doi: 10.1155/2021/5578568. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34335090 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical examination of immunoreactivity of transient receptor potential melastatin 2, glutathione peroxidase 4 and spexin in lichen planus.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Oct 14;316(10):675. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03417-y. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39400728 Review.
-
Increased expression of psoriasin (S100A7) and interleukin 17 (IL-17) in lesional skin in lichen planopilaris.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2024 Aug;41(4):364-371. doi: 10.5114/ada.2024.142179. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2024. PMID: 39290897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leonardi S., Cuppari C., Manti S., et al. Serum interleukin 17, interleukin 23, and interleukin 10 values in children with atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome (AEDS): association with clinical severity and phenotype. Allergy and Asthma Proceedings. 2015;36(1):74–81. doi: 10.2500/aap.2015.36.3808. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

