[Keratoconjunctivitis photoelectrica (arc eye)]
- PMID: 32774618
- PMCID: PMC7388637
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2020.36.42.19549
[Keratoconjunctivitis photoelectrica (arc eye)]
Abstract
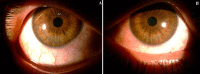
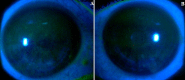
Photokeratitis is a painful keratitis caused by exposure of insufficiently protected eyes to the ultraviolet (UV) rays. We talk about "arc eye" when photokeratitis is caused by UV rays emitted by electric arc during electric arc welding process. We here report the case of a 35-year old rider, with no previous medical-surgical history, who had looked at an electric arc for a few minutes while the doors of his building were welded. He had bilateral burning in his eyes associated with lacrimation, photophobia and blepharospasm. Clinical examination showed corrected visual acuity of 8/10 and 9/10, conjunctival hyperemia with punctate erosive keratitis limited to palpebral fissure after the use of fluorescein. Given patient's clinical picture, keratoconjunctivitis photoelectrica (arc eye) was diagnosed. Treatment was based on topical antibiotics, wetting agents as well as agents with healing properties. Outcome was marked by total disappearance of the signs with restoration of bilateral visual acuity (10/10). This study highlights the role of prevention using appropriate protection equipment.
La photokératite est une kératite douloureuse causée par l'exposition non-protégée des yeux aux rayons ultraviolets (UV). On parle de «coup d'arc» quand la photokératite est induite par le rayonnement UV émis par l′arc électrique pendant le soudage à l′arc électrique. Nous rapportons le cas d′un patient de 35 ans, sans antécédents notables, cavalier de profession qui se dit avoir regardé pendant quelques minutes, un arc électrique durant le soudage des portes du stable suite à laquelle, il a présenté une douleur oculaire bilatérale à type de brûlure associé à des larmoiements photophobie et blépharospasme. Son examen clinique a montré une acuité visuelle avec correction à 8/10 et 9/10, une hyperhémie conjonctivale avec une kératite érosive ponctuée limité à la fente palpébrale après instillation de la fluorescéine. Vu le contexte, le diagnostic d'une kératoconjonctivite par coup d'arc a été retenu. Le patient a été mis sous antibiotique topique, agents mouillants et cicatrisants. L′évolution a été marquée, par la disparition totale des signes avec une acuité visuelle qui est remonté à 10/10 en bilatérale. A travers ce cas, on illustre l′intérêt d′une prévention par un port d′équipements de protection adaptés.
Keywords: Keratoconjunctivitis photoelectrica; arc eye; photokeratitis.
© Brahim Salem Joumany et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Les auteurs ne déclarent aucun conflit d'intérêts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retinal injury from a welding arc.Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 May;77(5):663-8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(74)90528-5. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974. PMID: 4823777 No abstract available.
-
[Antibiotic eye ointment with vitamin B and bandage. This helps keratoconjunctivitis photoelectrica].MMW Fortschr Med. 2002 Mar 14;144(11):37-8. MMW Fortschr Med. 2002. PMID: 12066508 German. No abstract available.
-
[Alterations of the anterior segment of the eye caused by exposure to UV radiation].Ophthalmologe. 2022 Mar;119(3):234-239. doi: 10.1007/s00347-021-01531-0. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Ophthalmologe. 2022. PMID: 34860283 Review. German.
-
Photokeratitis in Outdoor Event Participants Exposed to UV Radiation Display.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun 1;142(6):568-571. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.1092. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38696206 Free PMC article.
-
Photokeratitis and other phototoxic effects on the cornea and conjunctiva.Int J Toxicol. 2002 Nov-Dec;21(6):455-64. doi: 10.1080/10915810290169882. Int J Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 12537642 Review.
References
-
- Golu A, Gheorghisor I, Balasoiu A T, Balta F, Osiac E, Mogoanta L, et al. The effect of ultraviolet radiation on the cornea: experimental study. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2013;54(4):1115–1120. - PubMed
-
- Muresan S, Filip A, Muresan A, Şimon V, Moldovan R, Gal AF, et al. Histological findings in the Wistar rat cornea following UVB irradiation. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2013;54(2):247–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources