Targeting micro-RNAs by natural products: a novel future therapeutic strategy to combat cancer
- PMID: 32774718
- PMCID: PMC7407688
Targeting micro-RNAs by natural products: a novel future therapeutic strategy to combat cancer
Abstract
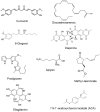
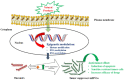
MicroRNAs are a class of short, non-coding RNAs that play a crucial role in normal physiology by attenuating translation or targeting messenger RNAs for degradation. Deregulation of miRNAs disturbs key molecular events in interconnected processes such as cell proliferation, tumor angiogenesis, self-renewal, apoptosis, metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. This process initiates, promotes and develops the pathophysiology of cancer. The modulation of miRNAs results in epigenetic changes in the genome, which eventually leads to cancer. Targeting deregulated miRNAs by natural products derived from plants is an ideal strategy to combat tumorigenesis. Owing to their fewer side effects, natural products have been used as chemotherapeutic agents against various cancers. These natural products modulate the dysregulated signaling pathways by downregulating the oncogenic miRNAs which play a crucial role in the development of tumorigenesis and maintain a fine balance of tumor suppressor miRNAs. This review article aims to highlight the key modifications of miRNAs which lead to tumorigenesis and the chemotherapeutic potential of natural products by targeting miRNAs and their possible mechanism of inhibition for developing an effective anti-cancer agent(s). They will have less damaging effects on normal cells for future chemotherapeutics.
Keywords: MicroRNA; cancer; metastasis; natural products; oncomirs; signalling.
AJTR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
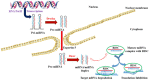
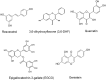
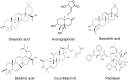
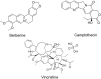
References
-
- Maher SG, Bibby BA, Moody HL, Reid G. Epigenetic Cancer Therapy. Elsevier; 2015. MicroRNAs and cancer; pp. 67–90.
-
- Kamphuis WW, Derada Troletti C, Reijerkerk A, Romero IA, de Vries HE. The blood-brain barrier in multiple sclerosis: microRNAs as key regulators. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015;14:157–167. - PubMed
-
- Ivkovic TC, Voss G, Cornella H, Ceder Y. microRNAs as cancer therapeutics: a step closer to clinical application. Cancer Lett. 2017;407:113–122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
