Th1 cytokines in conjunction with pharmacological Akt inhibition potentiate apoptosis of breast cancer cells in vitro and suppress tumor growth in vivo
- PMID: 32774769
- PMCID: PMC7392628
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.27556
Th1 cytokines in conjunction with pharmacological Akt inhibition potentiate apoptosis of breast cancer cells in vitro and suppress tumor growth in vivo
Abstract
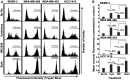
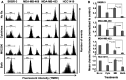
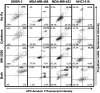
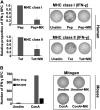
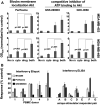
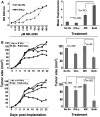
Targeted drug approaches have been a major focus for developing new anticancer therapies. Although many such agents approved in the last 20 years have improved outcomes, almost all have underperformed expectations. The full potential of such agents may yet be obtained through novel combinations. Previously, we showed that anti-estrogen drugs combined with a dendritic cell-based anti-HER-2 vaccine known to induce strong Th1-polarized immunity dramatically improved clinical response rates in patients with HER-2pos/ERpos early breast cancer. Here, we show that the small molecule Akt antagonist MK-2206, when combined with the Th1 cytokines IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, maximize indicators of apoptotic cell death in a panel of phenotypically-diverse human breast cancer lines. These findings were mirrored by other, structurally-unrelated Akt-targeting drugs that work through different mechanisms. Interestingly, we found that MK-2206, as well as the other Akt antagonist drugs, also had a tendency to suppress Th1 cytokine expression in stimulated human and murine lymphocytes, potentially complicating their use in conjunction with active immunotherapy. After verifying that MK-2206 plus IFN-gamma could show similar combined effects against breast cancer lines, even in the absence of TNF-alpha, we tested in a rodent HER-2pos breast cancer model either a HER-2-based DC vaccine, or recombinant IFN-gamma with or without MK-2206 administration. We found that for MK-2206, co-administration of recombinant IFN-gamma outperformed co-administration of DC vaccination for slowing tumor growth kinetics. These findings suggest a combined therapy approach for Akt-targeting drugs that incorporates recombinant Interferon-gamma and is potentially translatable to humans.
Keywords: Akt kinase; breast cancer; immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None.
Figures


References
-
- Oiseth SJM, Aziz S. Cancer Immunotherapy: a brief review of the history, possibilities, and challenges ahead. J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2017; 3:250–61. 10.20517/2394-4722.2017.41. - DOI
-
- Czerniecki B, Koski G, Koldovsky U, Xu S, Cohen P, Mick R, Nisenbaum H, Pasha T, Xu M, Fox K, Weinstein S, Orel S, Vonderheide R, et al. Targeting HER-2/neu in early breast cancer development using dendritic cells with staged interleukin-12 burst secretion. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:1842–52. 10.1158/0008-5472.can-06-4038. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharma A, Koldovsky U, Xu S, Mick R, Roses R, Fitzpatrick E, Weinstein S, Nisenbaum H, Levine BL, Fox K, Zhang P, Koski G, Czerniecki BJ. HER-2 pulsed dendritic cell vaccine can eliminate HER-2 expression and impact ductal carcinoma in situ . Cancer. 2012; 118:4354–62. 10.1002/cncr.26734. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

