cGAS-STING pathway in oncogenesis and cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 32774773
- PMCID: PMC7392626
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.27673
cGAS-STING pathway in oncogenesis and cancer therapeutics
Abstract
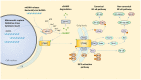
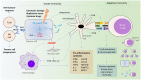
The host innate immunity offers the first line of defense against infection. However, recent evidence shows that the host innate immunity is also critical in sensing the presence of cytoplasmic DNA derived from genomic instability events, such as DNA damage and defective cell cycle progression. This is achieved through the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)/Stimulator of interferon (IFN) genes (STING) pathway. Here we discuss recent insights into the regulation of this pathway in cancer immunosurveillance, and the downstream signaling cascades that coordinate immune cell recruitment to the tumor microenvironment to destroy transformed cells through cellular senescence or cell death programs. Its central role in immunosurveillance positions the cGAS-STING pathway as an attractive anti-cancer immunotherapeutic drug target for chemical agonists or vaccine adjuvants and suggests a key node to be targeted in a synthetic lethal approach. We also discuss adaptive mechanisms used by cancer cells to circumvent cGAS-STING signaling and present evidence linking chronic cGAS-STING activation to inflammation-induced carcinogenesis, cautioning against the use of activating the cGAS-STING pathway as an anti-tumor immunotherapy. A deeper mechanistic understanding of the cGAS-STING pathway will aid in the identification of potentially efficacious anti-cancer therapeutic targets.
Keywords: STING; cGAS; cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; interferon; stimulator of interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- MacKenzie KJ, Carroll P, Martin CA, Murina O, Fluteau A, Simpson DJ, Olova N, Sutcliffe H, Rainger JK, Leitch A, Osborn RT, Wheeler AP, Nowotny M, et al. cGAS surveillance of micronuclei links genome instability to innate immunity. Nature. 2017; 548:461–465. 10.1038/nature23449. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials