Anti-cancer properties of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 against HT-29 colon cancer cells through regulation of Bax/Bcl-xL and AKT/PTEN signaling pathways
- PMID: 32774810
- PMCID: PMC7395184
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.43016.10115
Anti-cancer properties of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 against HT-29 colon cancer cells through regulation of Bax/Bcl-xL and AKT/PTEN signaling pathways
Abstract
Objectives: Chemotherapies used to treat colon cancer might often fail due to the emergence of chemoresistance and side effects. Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) is a beneficial probiotic, whose molecular mechanisms in the prevention of colon cancer are yet to be fully understood. The present study assessed the anti-cancer effects of EcN treatments in human colorectal cancer, HT-29 cell line, with the analysis of related mechanisms.
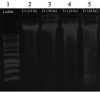
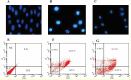
Materials and methods: The co-culture conditioned-media (CM) of EcN with adenocarcinoma HT-29 cells and heat-inactivated bacteria (HIB) were applied for the treatment of the HT-29 cells. To study the inhibition potential of CM and HIB on cancer cells, various cellular/molecular analyses were implemented, including DAPI-staining and DNA ladder assays, flow cytometry and Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR), as well as Western blotting analyses.
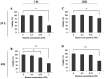
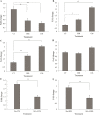
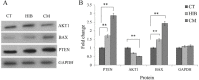
Results: Our results indicated that EcN could elicit apoptotic impacts on the colon cancer HT-29 cells by up-regulating PTEN and Bax and down-regulating AKT1 and Bcl-xL genes.
Conclusion: Based on our findings, EcN is proposed as a useful supplemental probiotic treatment against colon cancer.
Keywords: AKT; Apoptosis; Cell signaling; Colon cancer; Escherichia coli Nissle1917.
Figures

References
-
- Khiavi MA, Safary A, Aghanejad A, Barar J, Rasta SH, Golchin A, et al. Enzyme-conjugated gold nanoparticles for combined enzyme and photothermal therapy of colon cancer cells. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2019;572:333–344.
-
- Vahed SZ, Barzegari A, Saadat YR, Goreyshi A, Omidi Y. Leuconostoc mesenteroides-derived anticancer pharmaceuticals hinder inflammation and cell survival in colon cancer cells by modulating NF-κB/AKT/PTEN/MAPK pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;94:1094–1100. - PubMed
-
- Salmanzadeh R, Eskandani M, Mokhtarzadeh A, Vandghanooni S, Ilghami R, Maleki H, et al. Propyl gallate (PG) and tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ) may alter the potential anti-cancer behavior of probiotics. Food Biosci. 2018;24:37–45.
-
- Schultz M. Clinical use of E. coli Nissle. 1917 in;14:1012–1018. - PubMed
-
- Jafari B, Rezaie A, Alizadeh S. Isolation and identification of potentially probiotic bacteria from traditional dairy products of Ardabil region in Iran. Ann Biol Res. 2011;2:311–317.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
