Diagnosis of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in Emergency Department: Our experience
- PMID: 32774823
- PMCID: PMC7378380
- DOI: 10.4081/audiores.2020.232
Diagnosis of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in Emergency Department: Our experience
Abstract
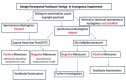
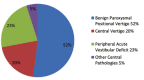
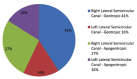
The Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) represents the first cause of peripheral vertigo in populations and it is determined by a displacement of otoconial fragments within the semicircular canals. Following the patient's head movements, these fragments, moving by inertia, incorrectly stimulate the canals generating vertigo. The BPPV is diagnosable by observing the nystagmus that is generated in the patient following the Dix-Hallpike maneuver used for BPPV diagnosis of vertical semi-circular canal, and, following the supine head yaw test used for lateral semi-circular canal. Correctly identifying the origin of this specific peripheral vertigo, would mean to obtain a faster diagnosis and an immediate resolution of the problem for the patient. In this context, this study aims to identify precise training activities, aimed at the application of specific diagnostic maneuverers for algorithm decisions in support of medical personnel. The evaluations reported in this study refer to the data collected in the Emergency Department of the Cardarelli Hospital of Naples. The results obtained, over a six-month observation period, highlighted the advantages of the proposed procedures in terms of costs, time and number of BPPV diagnoses.
Keywords: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; diagnostic algorithm; emergency department.
©Copyright: the Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Management of bilateral benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with Dix-Hallpike test].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Oct;53(10):764-7. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25567145 Chinese.
-
Clinical Practice Guideline: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Update).Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Mar;156(3_suppl):S1-S47. doi: 10.1177/0194599816689667. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017. PMID: 28248609
-
[Application of modified Dix-Hallpike maneuver in the diagnosis of posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Jun;33(6):512-514. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.06.009. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31163524 Chinese.
-
Classification, diagnostic criteria and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017 Feb;44(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2016.03.013. Epub 2016 May 9. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017. PMID: 27174206 Review.
-
Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008 Nov;139(5 Suppl 4):S47-81. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2008.08.022. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008. PMID: 18973840 Review.
References
-
- Lai YT, Wang TC, Chuang LJ, Chen MH, Wang PC. Epidemiology of vertigo: a National Survey. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2011;145:110-6. - PubMed
-
- Yin M, Ishikawa K, Wong WH, Shibata Y. A clinical epidemiological study in 2169 patients with vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx 2009;36:30-5. - PubMed
-
- Kerber KA, Meurer WJ, West BT, Fendrick AM. Dizziness presentations in U.S. emergency departments, 1995-2004. Acad Emerg Med 2008;15:744-50. - PubMed
-
- Post RE, Dickerson LM. Dizziness: a diagnostic approach. Am Fam Physician 2010;82:361-89. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
