Relationship between Serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels and Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy and Other Biomarkers
- PMID: 32774911
- PMCID: PMC7396029
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8480193
Relationship between Serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels and Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy and Other Biomarkers
Abstract
Aim: This study aims to measure serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in a sample of Jordanian patients and to determine their relationship with the different stages of diabetic retinopathy. It also explores the correlation between VEGF concentrations and different biochemical and demographic findings.
Materials and methods: A total of 167 adults participated in the study. Participants were divided into two main categories: patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) type 2 without diabetic retinopathy (DR) (N = 62) and patients with DM type 2 affected by DR (N = 105). DR patients were further subclassified into nonproliferative (N = 41) and proliferative (N = 64). Basic laboratory tests were measured to correlate with VEGF levels. Irisin, a hormone linked to diabetic retinopathy was also measured and correlated with VEGF.
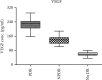
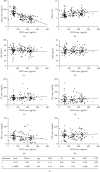
Results: Serum VEGF was found to positively correlate with the severity of diabetic retinopathy. The means of VEGF serum concentrations were 60 pg/mL for controls, 133 pg/mL for nonproliferative DR patients, and 229 pg/mL for proliferative DR patients. We found a significant positive correlation with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and a significant negative correlation with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels, age, and irisin.
Conclusion: In this cohort of Jordanian diabetics, serum VEGF concentrations strongly correlated with the presence and stages of diabetic retinopathy, suggesting it as an appropriate indicator for diabetic retinopathy early detection and management in this society. VEGF levels also significantly correlated with HbA1c, HDL, and irisin levels. Further studies are encouraged to explore these relationships in other ethnic groups and with different diabetic complications.
Copyright © 2020 Nakhleh E. Abu-Yaghi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest have been declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum inflammatory cytokines IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha and VEGF have influence on the development of diabetic retinopathy.Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2011 Apr-Jun;53(2):44-50. doi: 10.2478/v10153-010-0036-8. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2011. PMID: 21797106
-
Dysregulated Serum Lipid Metabolism Promotes the Occurrence and Development of Diabetic Retinopathy Associated With Upregulated Circulating Levels of VEGF-A, VEGF-D, and PlGF.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 22;8:779413. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.779413. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34904074 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma level of miR-93 is associated with higher risk to develop type 2 diabetic retinopathy.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017 Jun;255(6):1159-1166. doi: 10.1007/s00417-017-3638-5. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28382439
-
Serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels Correlate with Severity of Retinopathy in Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Dis Markers. 2019 Mar 24;2019:9401628. doi: 10.1155/2019/9401628. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31019585 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy.J Diabetes Complications. 2019 Dec;33(12):107417. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2019.107417. Epub 2019 Aug 15. J Diabetes Complications. 2019. PMID: 31669065 Review.
Cited by
-
Irisin Attenuates Pathological Neovascularization in Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Jun 1;63(6):21. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.6.21. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35737379 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Biopsy Combined with Multi-Omics Approaches in Diagnosis, Management, and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy.Biomedicines. 2025 May 26;13(6):1306. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061306. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On implications of somatostatin in diabetic retinopathy.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Sep 1;19(9):1984-1990. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.390955. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38227526 Free PMC article.
-
A Fluorescent Aptasensor Based on Assembled G-Quadruplex and Thioflavin T for the Detection of Biomarker VEGF165.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Nov 16;9:764123. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.764123. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34869275 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Hypoxia Inducible Factor -1 Alpha and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Level in Type 2 Diabetes Microvascular Complications and Development.Med Arch. 2022 Apr;76(2):135-139. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2022.76.135-139. Med Arch. 2022. PMID: 35774047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(1):S81–S90. - PubMed
-
- McCannel C. A. Retina-vitreous-macula. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 1999;74(10):1053–1054. doi: 10.4065/74.10.1053-b. - DOI
-
- Atlas D. International Diabetes Federation: IDF Diabetes Atlas. 7th. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

