The Use of Self-Inflating Hygroscopic Tissue Expanders to Facilitate Osteosarcoma Removal in a Massasauga Rattlesnake (Sistrurus catenatus)
- PMID: 32774984
- PMCID: PMC7407037
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8813911
The Use of Self-Inflating Hygroscopic Tissue Expanders to Facilitate Osteosarcoma Removal in a Massasauga Rattlesnake (Sistrurus catenatus)
Abstract
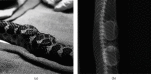
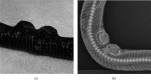
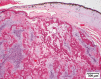
A 0.34 kg adult female Massasauga rattlesnake (Sistrurus catenatus) was presented for evaluation of a subcutaneous mass affecting the ventral scales. The mass was diagnosed as a sarcoma via punch biopsy with no evidence of metastasis on diagnostic imaging. Surgical margins of 1-2 cm were planned to achieve complete excision of the neoplasm. A technique for tissue expansion was employed due to concerns regarding the ability to close the surgical site without excess tension or dehiscence. Two 27 mm diameter × 5 mm hygroscopic self-inflating tissue expanders were placed subcutaneously under the lateral scales adjacent to the mass. Maximum skin expansion occurred over a four-week period, and no direct negative effects were noted. Excision of the primary mass was performed routinely five weeks after implant placement. Primary closure of the defect was achieved with minimal tension by incorporating the expanded skin. While the surgery was successful with no evidence of metastasis, the snake died of sepsis two weeks postoperatively. This is the first report of the use of self-inflating hygroscopic tissue expanders to help close a surgical defect in a reptile.
Copyright © 2020 Kate E. Archibald et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Validation of a shed skin corticosterone enzyme immunoassay in the African House Snake (Lamprophis fuliginosus) and its evaluation in the Eastern Massasauga Rattlesnake (Sistrurus catenatus catenatus).Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2013 Dec 1;194:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23994033
-
DISSEMINATED OPHIDIOMYCES OPHIODIICOLA INFECTION IN A CAPTIVE EASTERN MASSASAUGA (SISTRURUS CATENATUS CATENATUS).J Zoo Wildl Med. 2016 Mar;47(1):337-40. doi: 10.1638/2014-0222.1. J Zoo Wildl Med. 2016. PMID: 27010298
-
Outcome of reconstruction of cutaneous limb defects in dogs using hygroscopic "self-inflating" tissue expanders.J Small Anim Pract. 2018 Feb;59(2):98-105. doi: 10.1111/jsap.12766. Epub 2017 Nov 2. J Small Anim Pract. 2018. PMID: 29095498
-
In cold blood: Observational descriptive review of Eastern Massasauga rattlesnake bites reported to a single poison center over time.Toxicon. 2022 Jan 30;206:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2021.12.004. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Toxicon. 2022. PMID: 34914939 Review.
-
Hydrogel based soft tissue expanders for orodental reconstruction.Acta Biomater. 2023 Dec;172:53-66. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.10.021. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37866723 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
