Downregulation of microRNA-30c-5p was responsible for cell migration and tumor metastasis via COTL1-mediated microfilament arrangement in breast cancer
- PMID: 32775265
- PMCID: PMC7347814
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-20-472
Downregulation of microRNA-30c-5p was responsible for cell migration and tumor metastasis via COTL1-mediated microfilament arrangement in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer metastasis is the main problem that affects the therapy and prognosis of breast cancer patients. Studies have indicated the role of microRNAs in breast cancer regulation, but the mechanisms are largely unknown.
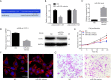
Methods: In this study, we determined the expression of microRNA-30c-5p (miR-30c-5p) and coactosin-like protein 1 (COTL1) gene in breast cancer tissues, and revealed their effects on breast cancer metastasis regulation. Breast cancer and paracancerous tissues were collected. Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to analyze the expression of miR-30c-5p and COTL1, and breast cancer cell line (MCF-7) was employed to verify the relationship between miR-30c-5p and COTL1. Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence were used for proteins analysis and microfilament observation, respectively. A dual-luciferase reporter gene was used for microRNA-gene interaction assay.
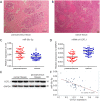
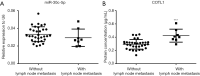
Results: The results showed that the expression of miR-30c-5p decreased, while the expression of COTL1 increased in breast cancer tissues. The results of luciferase reporting gene assay showed that, COTL1 was the target of miR-30c-5p. After miR-30c-5p was upregulated, the expression of COTL1 was reduced, microfilament arrangement was in disorder, and cell migration ability was inhibited. After miR-30c-5p was downregulated, the expression of COTL1 was increased, and the cell migration ability was enhanced. COTL1 protein expression levels were significantly higher in cancer tissues with lymph node metastasis.
Conclusions: These findings indicate that miR-30c-5p/COTL1 pathway regulates breast cancer metastasis and can be used as a potential therapy target.
Keywords: Breast cancer; cell migration ability; coactosin-like protein 1 (COTL1); microRNA-30c-5p (miR-30c-5p); microfilament.
2020 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/gs-20-472). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MiR-30c-5p suppresses migration, invasion and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer via targeting MTA1.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:554-560. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.084. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28686969
-
Transcriptome sequencing analysis reveals miR-30c-5p promotes ferroptosis in cervical cancer and inhibits growth and metastasis of cervical cancer xenografts by targeting the METTL3/KRAS axis.Cell Signal. 2024 May;117:111068. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111068. Epub 2024 Jan 27. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38286198
-
Genetic and epigenetic silencing of mircoRNA-506-3p enhances COTL1 oncogene expression to foster non-small lung cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):644-657. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13501. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27893417 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen triple helix repeat containing-1 negatively regulated by microRNA-30c promotes cell proliferation and metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jul 12;36(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0564-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28697793 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MicroRNA-30c in cancer progression.J Cancer. 2020 Feb 14;11(9):2593-2601. doi: 10.7150/jca.38449. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32201529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in breast cancer metastasis.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 May;12(5):1029-1046. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-00999-2. Epub 2021 May 13. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 33987801 Review.
-
Identification of miR-30c-5p microRNA in Serum as a Candidate Biomarker to Diagnose Endometriosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 3;25(3):1853. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031853. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339132 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression Profiles Analyzed Using Integrating RNA Sequencing, and Microarray Reveals Increased Inflammatory Response, Proliferation, and Osteoclastogenesis in Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 24;12:665442. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.665442. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34248943 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic Targets Regulated by Tumor-Suppressive miR-30c-1-3p and miR-30c-2-3p: TRIP13 Facilitates Cancer Cell Aggressiveness in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 21;15(16):4189. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164189. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627217 Free PMC article.
-
Coactosin-like protein 1 regulates integrity and repair of model intestinal epithelial barriers via actin binding dependent and independent mechanisms.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 8;12:1405454. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1405454. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39040043 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
