Dataset for homologous proteins in Drosophila melanogaster for SARS-CoV-2/human interactome
- PMID: 32775582
- PMCID: PMC7382932
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.106082
Dataset for homologous proteins in Drosophila melanogaster for SARS-CoV-2/human interactome
Abstract
Animal modelling for infectious diseases is critical to understand the biology of the pathogens including viruses and to develop therapeutic strategies against it. Herein, we present the sequence homology and expression data analysis of proteins found in Drosophila melanogaster that are orthologous to human proteins, reported as components of SARS-CoV-2/Human interactome. The dataset enlists sequence homology, query coverage, domain conservation, OrthoMCL and Ensembl Genome Browser support of 326 proteins in D.melanogaster that are potentially orthologous to 417 human proteins reported for their direct physical interactions with 28 proteins encoded by SARS-CoV-2 genome. Expression of these D.melanogaster orthologous genes in 26 anatomical positions are also plotted as heat maps in 27 sets, corresponding to the potential protein interactors for each viral protein. The data could be used to direct experiments and potentially predict their phenotypic and molecular outcome in order to dissect the biological roles and molecular functionality of SARS-CoV-2 proteins in a convenient animal model system like D.melanogaster.
Keywords: Animal modelling; COVID-19; Drosophila melanogaster; Interactome; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships which have, or could be perceived to have, influenced the work reported in this article.
Figures

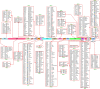
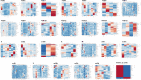
References
-
- Gordon D.E., Jang G.M., Bouhaddou M., Xu J., Obernier K., O'meara M.J., Guo J.Z., Swaney D.L., Tummino T.A., Huttenhain R., Kaake R.M. A SARS-CoV-2-human protein-protein interaction map reveals drug targets and potential drug-repurposing. Nature. 2020:1–3. doi: 10.1101/2020.03.22.002386. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chintapalli V., Wang J., Dow J. Using Flyatlas to identify better Drosophila models of human disease. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2008;3:S136–S137. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.04.331. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

