A GlycoGene CRISPR-Cas9 lentiviral library to study lectin binding and human glycan biosynthesis pathways
- PMID: 32776087
- PMCID: PMC8022984
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwaa074
A GlycoGene CRISPR-Cas9 lentiviral library to study lectin binding and human glycan biosynthesis pathways
Abstract
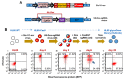
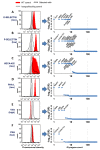
Glycan biosynthesis on cell surface proteins and lipids is orchestrated by different classes of enzymes and proteins including the following: i. glycosyltransferases that add saccharides; ii. glycosidases that trim glycans; iii. conserved oligomeric golgi complex members that regulate intracellular transport; iv. enzymes aiding the biosynthesis of sugar-nucleotides; and v. sulfotransferases. This manuscript describes a pooled "glycoGene CRISPR" lentiviral library that targets 347 human genes involved in the above processes. Approximately 10 single-guide RNA (sgRNA) are included against each glycogene, with the putative editing site spanning the length of the target. A data analysis scheme is presented in order to determine glycosylation pathways regulating biological processes. As proof of principle, forward genetic screen results are presented to identify penetrating glycogenes that regulate the binding of P-/E-selectin, anti-sialyl Lewis-X monoclonal antibody HECA-452 and selected lectins (phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin, vicia villosa lectin, peanut agglutinin) to HL-60 promyelocytic cells. Besides validating previously established biology, the study identifies three enzymes, PAPSS1, SLC35B2 and TPST2, as key molecules regulating sulfation of the major P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 in leukocytes. Approximately 80-90% of the sgRNA used in this study displayed high editing efficiency, and the CRISPR library picked up entire gene sets regulating specific biosynthetic pathways rather than only isolated genes. These data suggest that the glycoGene CRISPR library contains high-efficiency sgRNA. Further, this resource could be useful for the rapid screening of glycosylation-related genes and pathways that control lectin recognition in a variety of contexts.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; forward genetic screen; gene editing; glycoscience; selectin.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Cummings RD, McEver RP. 2015. C-type lectins. In: Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD, Stanley P, Hart GW, Aebi M, Darvill AG, Kinoshita T, Packer NH, Prestegard JH et al., editors. Essentials of glycobiology. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. p. 435–452. - PubMed
-
- Ellies LG, Tsuboi S, Petryniak B, Lowe JB, Fukuda M, Marth JD. 1998. Core 2 oligosaccharide biosynthesis distinguishes between selectin ligands essential for leukocyte homing and inflammation. Immunity. 9:881–890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

