Combined carbon photon and hydrogel therapy mediates the synergistic repair of full-thickness skin wounds
- PMID: 32776863
- PMCID: PMC7418267
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060520935326
Combined carbon photon and hydrogel therapy mediates the synergistic repair of full-thickness skin wounds
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated the synergistic repair effects of Prontosan hydrogel and carbon photon therapy in a rat full-thickness wound model.
Methods: The wavelength distribution of the photon source was determined. Dehydration of the Prontosan hydrogel and fibroblast viability were analyzed following exposure to different durations of light exposure at different distances from the source. Indexes of wound healing in a full-thickness rat wound model were then determined in groups (n = 8 each) subjected to either no treatment, Prontosan treatment only, carbon photon therapy only, or a combination of the two treatments (synergistic group).
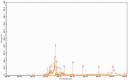
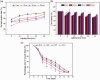
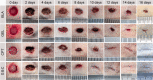
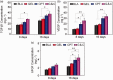
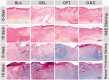
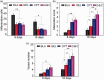
Results: Carbon photon exposure for 15 minutes at a distance of 20 cm from the wound was found to be optimal. Wound healing occurred faster in the synergistic group compared with the control and single-treatment groups. Growth factor secretion, granulation tissue formation, inflammation regulation, collagen deposition, and neovascularization were all higher in the synergistic group.
Conclusions: Prontosan hydrogel combined with carbon photon therapy may provide an optimal environment for wound healing and serve as a novel physical approach to the treatment of wounds. However, the number of animals included in this study was relatively small and a larger study is required to confirm these findings.
Keywords: Carbon photon therapy; collagen; fibroblasts; granulation tissue; growth factors; hydrogel; neovascularization; synergistic treatment; wound repair.
Figures

References
-
- Sorg H, Tilkorn DJ, Hager S, et al. Skin wound healing: an update on the current knowledge and concepts. Eur Surg Res 2017; 58: 81–94. - PubMed
-
- Lemmer B. Light and medicine. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 2016; 141: 1840–1844. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan BB. The carbon (formerly dark) reactions of photosynthesis. Photosynth Res 2016; 128: 215–217. - PubMed
-
- Yan JX, Liao X, Li SH, et al. Effects of carbon arc lamp irradiation on wound healing in a rat cutaneous full-thickness wound model. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg 2019; 37: 17–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

