Effect of Tropicamide on crystalline Lens rise in low-to-moderate myopic eyes
- PMID: 32778077
- PMCID: PMC7418382
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-020-01594-8
Effect of Tropicamide on crystalline Lens rise in low-to-moderate myopic eyes
Abstract
Background: Cycloplegics have been reported to induce changes in the lens thickness. However, the studies of correlation between cycloplegia and the lens position are limited. This study aims to investigate changes in crystalline lens rise (CLR) and other anterior segment parameters after inducing cycloplegia with tropicamide.
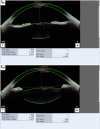
Methods: In this consecutive case study, 39 children (20 boys and 19 girls; mean age, 9.51 ± 1.75 years, mean spherical equivalence [SE], - 1.9 ± 1.5 D) with low-to moderate myopia were examined using CASIA 2 both before and after 30 min of administering 5-cycles (each 5 min apart) of 0.5% tropicamide. Measurements included CLR, crystalline lens thickness (CLT), mean radius of curvature of the anterior/posterior surface of the lens (Rf_ave/Rb_ave), anterior chamber depth (ACD), anterior chamber width (ACW), and central corneal thickness (CCT). Correlations of CLT and CLR with ACD, SE, and age were assessed respectively.
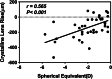
Results: CLT and CLR decreased significantly after cycloplegia (p < 0.001 and p < 0.001, respectively); whereas CCT, ACD, and Rf_ave increased (p = 0.008, p < 0.001, p < 0.001, respectively). A positive correlation was found between CLR and SE (r = 0.565, p < 0.001). However, a negative correlation between ACD and CLR was found before and after cycloplegia (r = - 0.430, p = 0.006; r = - 0.342, p = 0.035, respectively).
Conclusions: The crystalline lens appeared thinner and moved backward after cycloplegia. ACD increased mainly due to the backward movement of the crystalline lens. These results aid in elucidating the impact of crystalline lens changes during the process of accommodation.
Keywords: Crystalline Lens rise; Myopia; Tropicamide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest and have no proprietary interest in any of the materials mentioned in this article.
Figures

References
-
- Edwards MH, Lam CS. The epidemiology of myopia in Hong Kong. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2004;33:34–38. - PubMed
-
- Lin LL, Shih YF, Hsiao CK, Chen CJ, Lee LA, Hung PT. Epidemiologic study of the prevalence and severity of myopia among schoolchildren in Taiwan in 2000. J Formos Med Assoc. 2001;100:684–691. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

