Proportional modes of ventilation: technology to assist physiology
- PMID: 32780167
- PMCID: PMC7417783
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-020-06206-z
Proportional modes of ventilation: technology to assist physiology
Abstract
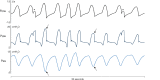
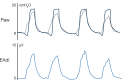
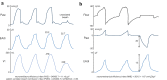
Proportional modes of ventilation assist the patient by adapting to his/her effort, which contrasts with all other modes. The two proportional modes are referred to as neurally adjusted ventilatory assist (NAVA) and proportional assist ventilation with load-adjustable gain factors (PAV+): they deliver inspiratory assist in proportion to the patient's effort, and hence directly respond to changes in ventilatory needs. Due to their working principles, NAVA and PAV+ have the ability to provide self-adjusted lung and diaphragm-protective ventilation. As these proportional modes differ from 'classical' modes such as pressure support ventilation (PSV), setting the inspiratory assist level is often puzzling for clinicians at the bedside as it is not based on usual parameters such as tidal volumes and PaCO2 targets. This paper provides an in-depth overview of the working principles of NAVA and PAV+ and the physiological differences with PSV. Understanding these differences is fundamental for applying any assisted mode at the bedside. We review different methods for setting inspiratory assist during NAVA and PAV+ , and (future) indices for monitoring of patient effort. Last, differences with automated modes are mentioned.
Keywords: Inspiratory assist; Mechanical ventilation; Proportional modes; Respiratory effort.
Conflict of interest statement
AHJ reports personal fees from Liberate Medical, outside the submitted work. GC reports personal fees from Air Liquide Medical System, personal fees from Löwenstein, outside the submitted work. LH has received grants from Orion Pharma and Liberate Medical and speakers fee from Getinge. LB conducts an investigator-initiated trial on PAV+ (NCT02447692) funded by the Canadian Institute for Health Research and a partnership with Medtronic Covidien; his laboratory also receives grants and non-financial support from Fisher & Paykel, non-financial support from Air Liquide Medical System, non-financial support from Philips, non-financial support from Sentec, other from General Electric. Other authors have nothing to declare.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

