A human circulating immune cell landscape in aging and COVID-19
- PMID: 32780218
- PMCID: PMC7417788
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-020-00762-2
A human circulating immune cell landscape in aging and COVID-19
Abstract
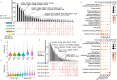
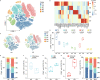
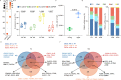
Age-associated changes in immune cells have been linked to an increased risk for infection. However, a global and detailed characterization of the changes that human circulating immune cells undergo with age is lacking. Here, we combined scRNA-seq, mass cytometry and scATAC-seq to compare immune cell types in peripheral blood collected from young and old subjects and patients with COVID-19. We found that the immune cell landscape was reprogrammed with age and was characterized by T cell polarization from naive and memory cells to effector, cytotoxic, exhausted and regulatory cells, along with increased late natural killer cells, age-associated B cells, inflammatory monocytes and age-associated dendritic cells. In addition, the expression of genes, which were implicated in coronavirus susceptibility, was upregulated in a cell subtype-specific manner with age. Notably, COVID-19 promoted age-induced immune cell polarization and gene expression related to inflammation and cellular senescence. Therefore, these findings suggest that a dysregulated immune system and increased gene expression associated with SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility may at least partially account for COVID-19 vulnerability in the elderly.
Keywords: COVID-19; aging; blood; immune cells; single-cell sequencing.
Figures












Comment in
-
The impact of aging and COVID-19 on our immune system: a high-resolution map from single cell analysis.Protein Cell. 2020 Oct;11(10):703-706. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00782-y. Protein Cell. 2020. PMID: 32894404 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bahar R, Hartmann CH, Rodriguez KA, Denny AD, Busuttil RA, Dollé ME, Calder RB, Chisholm GB, Pollock BH, Klein CA, et al. Increased cell-to-cell variation in gene expression in ageing mouse heart. Nature. 2006;441(7096):1011–1014. - PubMed
-
- Bian H, Zheng Z, Wei D, et al (2020) Meplazumab treats COVID-19 pneumonia: an open-labelled, concurrent controlled add-on clinical trial. medRxiv: 2020.03.21.20040691.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

