Pharmacogenetics for severe adverse drug reactions induced by molecular-targeted therapy
- PMID: 32780457
- PMCID: PMC7540972
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.14609
Pharmacogenetics for severe adverse drug reactions induced by molecular-targeted therapy
Abstract
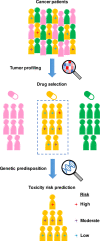
Molecular-targeted drugs specifically interfere with molecules that are frequently overexpressed or mutated in cancer cells. As such, these drugs are generally considered to precisely attack cancer cells, thereby inducing fewer adverse drug reactions (ADRs). However, molecular-targeted drugs can still cause characteristic ADRs that, although rarely severe, can be life-threatening. Therefore, it is becoming increasingly important to be able to predict which patients are at risk of developing ADRs after treatment with molecular-targeted therapy. The emerging field of pharmacogenetics aims to better distinguish the genetic variants associated with drug toxicity and efficacy to improve the selection of therapeutic strategies for each genetic profile. Here, we provide an overview of the current reports on the relationship between genetic variants and molecular-targeted drug-induced severe ADRs in oncology.
Keywords: adverse drug reaction; molecular-targeted drug; pharmacogenetics; polymorphism; precision medicine.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abbas Z, Rehman S. An overview of cancer treatment modalities In: Neoplasm. IntechOpen; 2018. 10.5772/intechopen.76558 - DOI
-
- Ogimoto A, Okayama H, Nagai T, et al. Pharmacogenetic interactions between Angiotensin‐converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and response to cibenzoline in patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010;55:506‐510. - PubMed
-
- Plaza‐Serón MDC, Ayuso P, Pérez‐Sánchez N, et al. Copy number variation in ALOX5 and PTGER1 is associated with NSAIDs‐induced urticaria and/or angioedema. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2016;26:280‐287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials