Golimumab in adolescents with Crohn's disease refractory to previous tumour necrosis factor antibody
- PMID: 32781480
- PMCID: PMC7891654
- DOI: 10.1111/apa.15522
Golimumab in adolescents with Crohn's disease refractory to previous tumour necrosis factor antibody
Abstract
Aim: Anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α drugs are effective treatments for the management of moderate/severe Crohn's disease (CD), but treatment failure is common. In the treatment of paediatric CD, there are no data about the use of a third introduced subcutaneous TNF antibody golimumab.
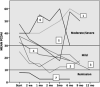
Methods: We evaluated the efficacy of golimumab for adolescents with moderate/severe CD. Retrospective analyses were done in all 7 (5 girls) adolescents who received golimumab at a median age of 17 years for a median of 7.2 months. Paediatric Crohn's disease activity index (PCDAI), full blood count, inflammatory markers, use of corticosteroids and adverse events were recorded.
Results: With golimumab, 5 of the 7 children were PCDAI responders and 2 entered remission (PCDAI <10). Faecal calprotectin was significantly reduced after 4 weeks compared to baseline. Out of five children, steroid withdrawal was possible in one and steroid reduction in two cases. There were no serious side effects.
Conclusion: In moderate/severe CD, golimumab induced clinical remission with PCDAI response. Golimumab may be an effective rescue therapy in refractory CD.
Keywords: Crohn's disease; adolescents; clinical response; golimumab.
© 2020 The Authors. Acta Paediatrica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Foundation Acta Paediatrica.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no financial or personal relationship with other people or organisations that could inappropriately influence this work. There were no financial or personal relationships with any company or organisation sponsoring the research at the time the research was done.
References
-
- Markowitz J, Grancher K, Kohn N, et al. A multicenter trial of 6‐mercaptopurine and prednisone in children with newly diagnosed crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2000;119(4):895‐902. - PubMed
-
- Bell SJ, Kamm MA. Review article: the clinical role of anti‐TNFalpha antibody treatment in crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000;14(5):501‐514. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical