Arginine and Endothelial Function
- PMID: 32781796
- PMCID: PMC7460461
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8080277
Arginine and Endothelial Function
Abstract
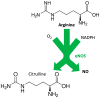
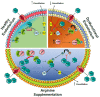
Arginine (L-arginine), is an amino acid involved in a number of biological processes, including the biosynthesis of proteins, host immune response, urea cycle, and nitric oxide production. In this systematic review, we focus on the functional role of arginine in the regulation of endothelial function and vascular tone. Both clinical and preclinical studies are examined, analyzing the effects of arginine supplementation in hypertension, ischemic heart disease, aging, peripheral artery disease, and diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: ADMA; BH4; COVID-19; L-arginine; NADPH; arginine; arginine paradox; blood pressure; dietary supplements; eNOS uncoupling; endothelial dysfunction; endothelium; heart failure; hypertension; myocardial infarction; nitric oxide; oxidative stress; peripheral artery disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the paper.
Figures
References
-
- Lopez M.J., Mohiuddin S.S. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2020. Biochemistry, Essential Amino Acids. - PubMed
-
- Serpe M.J., Zhang X. The Principles, Development and Application of Microelectrodes for the In Vivo Determination of Nitric Oxide. In: Michael A.C., Borland L.M., editors. Electrochemical Methods for Neuroscience. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

