Targetable ERBB2 mutation status is an independent marker of adverse prognosis in estrogen receptor positive, ERBB2 non-amplified primary lobular breast carcinoma: a retrospective in silico analysis of public datasets
- PMID: 32782013
- PMCID: PMC7422515
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-020-01324-4
Targetable ERBB2 mutation status is an independent marker of adverse prognosis in estrogen receptor positive, ERBB2 non-amplified primary lobular breast carcinoma: a retrospective in silico analysis of public datasets
Abstract
Background: Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) accounts for 10-15% of primary breast cancers and is typically estrogen receptor alpha positive (ER+) and ERBB2 non-amplified. Somatic mutations in ERBB2/3 are emerging as a tractable mechanism underlying enhanced human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2) activity. We tested the hypothesis that therapeutically targetable ERBB2/3 mutations in primary ILC of the breast associate with poor survival outcome in large public datasets.
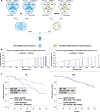
Methods: We performed in silico comparison of ERBB2 non-amplified cases of ER+ stage I-III primary ILC (N = 279) and invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC, N = 1301) using METABRIC, TCGA, and MSK-IMPACT information. Activating mutations amenable to HER2-directed therapy with neratinib were identified using existing functional data from in vitro cell line and xenograft experiments. Multivariate analysis of 10-year overall survival (OS) with tumor size, grade, and lymph node status was performed using a Cox regression model. Differential gene expression analyses by ERBB2 mutation and amplification status was performed using weighted average differences and an in silico model of response to neratinib derived from breast cancer cell lines.
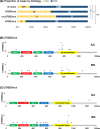
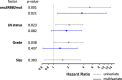
Results: ILC tumors comprised 17.7% of all cases in the dataset but accounted for 47.1% of ERBB2-mutated cases. Mutations in ERBB2 were enriched in ILC vs. IDC cases (5.7%, N = 16 vs. 1.4%, N = 18, p < 0.0001) and clustered in the tyrosine kinase domain of HER2. ERBB3 mutations were not enriched in ILC (1.1%, N = 3 vs. 1.8%, N = 23; p = 0.604). Median OS for patients with ERBB2-mutant ILC tumors was 66 months vs. 211 months for ERBB2 wild-type (p = 0.0001), and 159 vs. 166 months (p = 0.733) for IDC tumors. Targetable ERBB2 mutational status was an independent prognostic marker of 10-year OS-but only in ILC (hazard ratio, HR = 3.7, 95% CI 1.2-11.0; p = 0.021). Findings were validated using a novel ERBB2 mutation gene enrichment score (HR for 10-year OS in ILC = 2.3, 95% CI 1.04-5.05; p = 0.040).
Conclusions: Targetable ERBB2 mutations are enriched in primary ILC and their detection represents an actionable strategy with the potential to improve patient outcomes. Biomarker-led clinical trials of adjuvant HER-targeted therapy are warranted for patients with ERBB2-mutated primary ILC.
Keywords: Adjuvant; Breast cancer; ERBB2; HER2; Lobular; Mutation; Prognosis; Therapeutic biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
Since the first submission of the article, the corresponding author (SJJ) has moved employment to AstraZeneca, with no competing interests to declare. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of Stromal Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes and Genomic Alterations in Metastatic Lobular Breast Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 1;26(23):6254-6265. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2268. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32943456
-
ERBB2 mutation is associated with a worse prognosis in patients with CDH1 altered invasive lobular cancer of the breast.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80655-80663. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13019. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27811364 Free PMC article.
-
Relative effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy for invasive lobular compared with invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast.Cancer. 2017 Aug 15;123(16):3015-3021. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30699. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28382636
-
Comprehensive Review of Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Features of Invasive Lobular Cancer.Oncologist. 2021 Jun;26(6):e943-e953. doi: 10.1002/onco.13734. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Oncologist. 2021. PMID: 33641217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and future diagnostic and treatment strategies for patients with invasive lobular breast cancer.Ann Oncol. 2022 Aug;33(8):769-785. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.05.006. Epub 2022 May 21. Ann Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35605746 Review.
Cited by
-
Co-occurring gain-of-function mutations in HER2 and HER3 modulate HER2/HER3 activation, oncogenesis, and HER2 inhibitor sensitivity.Cancer Cell. 2021 Aug 9;39(8):1099-1114.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Cancer Cell. 2021. PMID: 34171264 Free PMC article.
-
The Genomic Landscape of Lobular Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 18;13(8):1950. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081950. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919581 Free PMC article.
-
TCGAnalyzeR: An Online Pan-Cancer Tool for Integrative Visualization of Molecular and Clinical Data of Cancer Patients for Cohort and Associated Gene Discovery.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 13;16(2):345. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020345. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254834 Free PMC article.
-
ERBB2 promoter demethylation and immune cell infiltration promote a poor prognosis for cancer patients.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 12;12:1012138. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1012138. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36172165 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into E-Cadherin Impairment in CDH1-Unaltered Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Bioinformatic Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 17;25(16):8961. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168961. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martinez V, Azzopardi JG. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: incidence and variants. Histopathology. 1979;3(6):467–488. - PubMed
-
- Li CI, Anderson BO, Daling JR, Moe RE. Trends in incidence rates of invasive lobular and ductal breast carcinoma. JAMA. 2003;289(11):1421–1424. - PubMed
-
- Li CI, Daling JR. Changes in breast cancer incidence rates in the United States by histologic subtype and race/ethnicity, 1995 to 2004. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2007;16(12):2773–2780. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, Pineros M, et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(8):1941–1953. - PubMed
-
- Pestalozzi BC, Zahrieh D, Mallon E, Gusterson BA, Price KN, Gelber RD, et al. Distinct clinical and prognostic features of infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: combined results of 15 International Breast Cancer Study Group clinical trials. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(18):3006–3014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

