Circ_0007841 promotes the progression of multiple myeloma through targeting miR-338-3p/BRD4 signaling cascade
- PMID: 32782441
- PMCID: PMC7414763
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01475-6
Circ_0007841 promotes the progression of multiple myeloma through targeting miR-338-3p/BRD4 signaling cascade
Abstract
Background: The pathogenesis of multiple myeloma (MM) is not completely known. Uncovering the potential mechanism of MM initiation and progression is essential for identifying novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets. Herein, we explored the function and the working mechanism of circular RNA circ_0007841 in MM progression.
Methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was employed to detect the expression of circ_0007841, microRNA-338-3p (miR-338-3p) and bromodomain containing 4 (BRD4). Cell proliferation ability was analyzed through cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) assay, colony formation assay and flow cytometry. Transwell assays were conducted to measure the migration and invasion abilities of MM cells. Cell apoptosis was also assessed by flow cytometry. The interaction between miR-338-3p and circ_0007841 or BRD4 was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA-pull down assay.
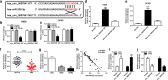
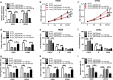
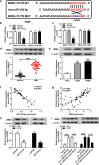
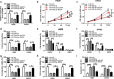
Results: Circ_0007841 was highly expressed in bone marrow (BM)-derived plasma cells of MM patients and MM cell lines than that in healthy volunteers and normal plasma cell line nPCs. Circ_0007841 promoted the proliferation, cell cycle and metastasis and impeded the apoptosis of MM cells. miR-338-3p was a direct target of circ_0007841 in MM cells and circ_0007841 accelerated the progression of MM through targeting miR-338-3p. BRD4 could directly bind to miR-338-3p in MM cells and miR-338-3p exerted an anti-tumor role through targeting BRD4. Circ_0007841 promoted the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling via miR-338-3p/BRD4 axis. Exosomes generated from mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) elevated the malignant behaviors of MM cells via circ_0007841.
Conclusion: Circ_0007841 acted as an oncogene to promote the proliferation, cell cycle and motility and restrain the apoptosis of MM cells through sequestering miR-338-3p to up-regulate the expression of BRD4.
Keywords: BRD4; Exosome; Multiple myeloma; circ_0007841; miR-338-3p.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Gertz MA. Multiple myeloma—a cure within reach. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018;59(11):2521–2523. - PubMed
-
- Yong K, Gonzalez-McQuire S, Szabo Z, Schoen P, Hajek R. The start of a new wave: developments in proteasome inhibition in multiple myeloma. Eur J Haematol. 2018 - PubMed
-
- Yuen HLA, Low MSY, Fedele P, Kalff A, Walker P, Bergin K, Coutsouvelis J, Grigoriadis G, Spencer A. DCEP as a bridge to ongoing therapies for advanced relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018;59(12):2842–2846. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

