Proof of Concept for a New Raman-Based Prototype for Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring
- PMID: 32783466
- PMCID: PMC7783007
- DOI: 10.1177/1932296820947112
Proof of Concept for a New Raman-Based Prototype for Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring
Abstract
Background: Noninvasive glucose monitoring (NIGM) in diabetes is a long-sought-for technology. Among the many attempts Raman spectroscopy was considered as the most promising because of its glucose specificity. In this study, a recently developed prototype (GlucoBeam, RSP Systems A/S, Denmark) was tested in patients with type 1 diabetes to establish calibration models and to demonstrate proof of concept for this device in real use.
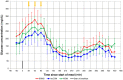
Methods: The NIGM table-top prototype was used by 15 adult subjects with type 1 diabetes for up to 25 days at home and in an in-clinic setting. On each day, the subjects performed at least six measurement units throughout the day. Each measurement unit comprised two capillary blood glucose measurements, two scans with an intermittent scanning continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system, and two NIGM measurements using the thenar of the subject's right hand.
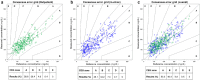
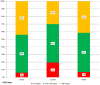
Results: Calibration models were established using data from 19 to 24 days. The remaining 3-8 days were used for independent validation. The mean absolute relative difference of the NIGM prototype was 23.6% ± 13.1% for the outpatient days, 28.2% ± 9.9% for the in-clinic day, and 26.3% ± 10.8% for the complete study. Consensus error grid analysis of the NIGM prototype for the complete study showed 93.6% of values in clinically acceptable zones A and B.
Conclusions: This proof of concept study demonstrated a practical realization of a Raman-based NIGM device, with performance on par with early-generation CGM systems. The findings will assist in further performance improvements of the device.
Keywords: Raman spectroscopy; continuous glucose monitoring; mean absolute relative difference; noninvasive glucose monitoring; performance; self-monitoring of blood glucose.
Conflict of interest statement
SP, SS, NJ, EZ, ML, and CH are employees of IfDT.
KDH receives a consultant fee as Scientific Advisor for RSP Systems.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9th ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2019.
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes 2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(suppl 1):S1-S156. - PubMed
-
- Delbeck S, Vahlsing T, Leonhardt S, Steiner G, Heise HM. Non-invasive monitoring of blood glucose using optical methods for skin spectroscopy-opportunities and recent advances. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411(1):63-77. - PubMed
-
- Freckmann G. Basics and use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in diabetes therapy. J Lab Med. 2020;44(2): 71-79.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

