Velocity Pulsatility and Arterial Distensibility Along the Internal Carotid Artery
- PMID: 32783485
- PMCID: PMC7660833
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016883
Velocity Pulsatility and Arterial Distensibility Along the Internal Carotid Artery
Abstract
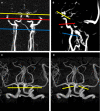
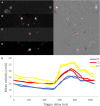
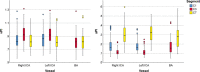
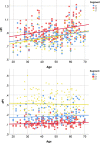
Background Attenuation of velocity pulsatility along the internal carotid artery (ICA) is deemed necessary to protect the microvasculature of the brain. The role of the carotid siphon within the whole ICA trajectory in pulsatility attenuation is still poorly understood. This study aims to assess arterial variances in velocity pulsatility and distensibility over the whole ICA trajectory, including effects of age and sex. Methods and Results We assessed arterial velocity pulsatility and distensibility using flow-sensitized 2-dimensional phase-contrast 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging in 118 healthy participants. Velocity pulsatility index (vPI=(Vmax-Vmin)/Vmean) and arterial distensibility defined as area pulsatility index (Amax-Amin)/Amean) were calculated at C1, C3, and C7 segments of the ICA. vPI increased between C1 and C3 (0.85±0.13 versus 0.93±0.13, P<0.001 for averaged right+left ICA) and decreased between C3 and C7 (0.93±0.13 versus 0.84±0.13, P<0.001) with overall no effect (C1-C7). Conversely, the area pulsatility index decreased between C1 and C3 (0.18±0.06 versus 0.14±0.04, P<0.001) and increased between C3 and C7 (0.14±0.04 versus 0.31±0.09, P<0.001). vPI in men is higher than in women and increases with age (P<0.015). vPI over the carotid siphon declined with age but remained stable over the whole ICA trajectory. Conclusions Along the whole ICA trajectory, vPI increased from extracranial C1 up to the carotid siphon C3 with overall no effect on vPI between extracranial C1 and intracranial C7 segments. This suggests that the bony carotid canal locally limits the arterial distensibility of the ICA, increasing the vPI at C3 which is consequently decreased again over the carotid siphon. In addition, vPI in men is higher and increases with age.
Keywords: MRI angiography; cerebral hemodynamics; distensibility; internal carotid artery; velocity pulsatility index.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood Flow Velocity Pulsatility and Arterial Diameter Pulsatility Measurements of the Intracranial Arteries Using 4D PC-MRI.Neuroinformatics. 2022 Apr;20(2):317-326. doi: 10.1007/s12021-021-09526-7. Epub 2021 May 21. Neuroinformatics. 2022. PMID: 34019208 Free PMC article.
-
Does the Internal Carotid Artery Attenuate Blood-Flow Pulsatility in Small Vessel Disease? A 7 T 4D-Flow MRI Study.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Aug;56(2):527-535. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28062. Epub 2022 Jan 7. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34997655 Free PMC article.
-
Dampening of blood-flow pulsatility along the carotid siphon: does form follow function?AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011 Jun-Jul;32(6):1107-12. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2426. Epub 2011 Apr 7. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. PMID: 21474624 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced flow velocity in the internal carotid artery independently of cardiac hemodynamics in patients with cerebral ischemia.J Clin Ultrasound. 2007 Jul-Aug;35(6):314-21. doi: 10.1002/jcu.20332. J Clin Ultrasound. 2007. PMID: 17427213
-
Aplasia of the internal carotid artery.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2003 Feb;145(2):117-25; discussion 125. doi: 10.1007/s00701-002-1046-y. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2003. PMID: 12601459 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Intracranial Arterial Pulsatility and Microvascular Brain Damage in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024 Apr 8;45(4):386-392. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8212. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 38548304 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of arterial pulsatility of cerebral perforating arteries using 7T high-resolution dual-VENC phase-contrast MRI.Magn Reson Med. 2024 Aug;92(2):605-617. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30073. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Magn Reson Med. 2024. PMID: 38440807 Free PMC article.
-
Normative Cerebral Hemodynamics in Middle-aged and Older Adults Using 4D Flow MRI: Initial Analysis of Vascular Aging.Radiology. 2023 May;307(3):e222685. doi: 10.1148/radiol.222685. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Radiology. 2023. PMID: 36943077 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Flow Velocity Pulsatility and Arterial Diameter Pulsatility Measurements of the Intracranial Arteries Using 4D PC-MRI.Neuroinformatics. 2022 Apr;20(2):317-326. doi: 10.1007/s12021-021-09526-7. Epub 2021 May 21. Neuroinformatics. 2022. PMID: 34019208 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Vascular Properties With the Brain White Matter Hyperintensity in Middle-Aged Population.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Jun 7;11(11):e024606. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.024606. Epub 2022 May 27. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35621212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Humphrey JD, Na S. Elastodynamics and arterial wall stress. Ann Biomed Eng. 2002;30:509–523. - PubMed
-
- Gaballa MA, Jacob CT, Raya TE, Liu J, Simon B, Goldman S. Large artery remodeling during aging: biaxial passive and active stiffness. Hypertension. 1998;32:437–443. - PubMed
-
- O'Rourke MF, Hashimoto J. Mechanical factors in arterial aging: a clinical perspective. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Jagtap A, Gawande S, Sharma S. Biomarkers in vascular dementia: a recent update. Biomarkers Genomic Med. 2015;7:43–56.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

