Optimisation of tube voltage range (kVp) for AP abdomen, pelvis and spine imaging of average patients with a digital radiography (DR) imaging system using a computer simulator
- PMID: 32783630
- PMCID: PMC7548356
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20200565
Optimisation of tube voltage range (kVp) for AP abdomen, pelvis and spine imaging of average patients with a digital radiography (DR) imaging system using a computer simulator
Abstract
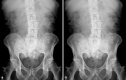
Objectives: To investigate via computer simulation, an optimised tube voltage (kVp) range for caesium iodide (CsI)-based digital radiography (DR) of the abdomen, pelvis and lumbar spine.
Methods: Software capable of simulating abdomen, pelvis and spine radiographs was used. Five evaluators graded clinical image criteria in images of 20 patients at tube voltages ranging from 60 to 120 kVp in 10 kVp increments. These criteria were scored blindly against the same patient reconstructed at a specific reference kVp. Linear mixed effects analysis was used to evaluate image scores for each criterion and test for statistical significance.
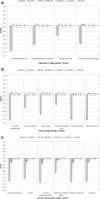
Results: Score was dependent on tube voltage and image criteria; both were statistically significant. All criteria for all anatomies scored very poorly at 60 kVp. Scores for abdomen, pelvis and spine imaging peaked at 70, 70 and 100 kVp, respectively, but other kVp values were not significantly poorer.
Conclusions: Results indicate optimum tube voltages of 70 kVp for abdomen and pelvis (with an optimum range 70-120 kVp), and 100 kVp (optimum range 80-120 kVp) for lumbar spine.
Advances in knowledge: There are no recommendations for optimised tube voltage parameters for DR abdomen, pelvis or lumbar spine imaging. This study has investigated and recommended an optimal tube voltage range.
Figures
References
-
- Moore CS, Liney GP, Beavis AW, Saunderson JR. A method to produce and validate a digitally reconstructed radiograph-based computer simulation for optimisation of chest radiographs acquired with a computed radiography imaging system. Br J Radiol 2011; 84: 890–902. doi: 10.1259/bjr/30125639 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moore CS, Wood TJ, Saunderson JR, Beavis AW. A method to incorporate the effect of beam quality on image noise in a digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRr) based computer simulation for optimisation of digital radiography. Phys Med Biol 2017; 62: 7379–93. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aa81fb - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moore CS, Avery G, Balcam S, Needler L, Swift A, Beavis AW, et al. . Use of a digitally reconstructed radiograph-based computer simulation for the optimisation of chest radiographic techniques for computed radiography imaging systems. Br J Radiol 2012; 85: e630–9. doi: 10.1259/bjr/47377285 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jacobs SJ, Kuhl LA, Xu G, Powell R, Paterson DR, C K C N. Optimum tube voltage for pelvic direct radiography: a phantom study. The South African Radiographer 2015; 53.

