An Integrated Strategy for the Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Healthcare Workers: A Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 32785110
- PMCID: PMC7460144
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17165785
An Integrated Strategy for the Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Healthcare Workers: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Since the beginning of SARS-CoV-2 outbreak, a large number of infections have been reported among healthcare workers (HCWs). The aim of this study was to investigate the occurrence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among HCWs involved in the first management of infected patients and to describe the measures adopted to prevent the transmission in the hospital.
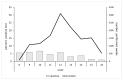
Methods: This prospective observational study was conducted between February 21 and April 16, 2020, in the Padua University Hospital (north-east Italy). The infection control policy adopted consisted of the following: the creation of the "Advanced Triage" area for the evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 cases, and the implementation of an integrated infection control surveillance system directed to all the healthcare personnel involved in the Advance Triage area. HCWs were regularly tested with nasopharyngeal swabs for SARS-CoV-2; body temperature and suggestive symptoms were evaluated at each duty. Demographic and clinical data of both patients and HCWs were collected and analyzed; HCWs' personal protective equipment (PPE) consumption was also recorded. The efficiency of the control strategy among HCWs was evaluated identifying symptomatic infection (primary endpoint) and asymptomatic infection (secondary endpoint) with confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2.
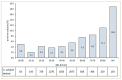
Results: 7595 patients were evaluated in the Advanced Triage area: 5.2% resulted positive and 72.4% was symptomatic. The HCW team was composed of 60 members. A total of 361 nasopharyngeal swabs were performed on HCWs. All the swabs resulted negative and none of the HCWs reached the primary or the secondary endpoint.
Conclusions: An integrated hospital infection control strategy, consisting of dedicated areas for infected patients, strict measures for PPE use and mass surveillance, is successful to prevent infection among HCWs.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; health care workers; infection control; novel coronavirus; personal protective equipment; respiratory protective device.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Spiteri G., Fielding J., Diercke M., Campese C., Enouf V., Gaymard A., Bella A., Sognamiglio P., Sierra Moros M.J., Riutort A.N., et al. First cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the WHO European Region, 24 January to 21 February 2020. Eurosurveillance. 2020;25:1–5. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.9.2000178. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Outbreak of novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID19): Situation in Italy–23 February 2020. [(accessed on 5 August 2020)];ECDC. 2020 Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/video-ecdc-statement-sit....
-
- Civil Protection Department-Coronavirus Emergency Press Releases. [(accessed on 20 May 2020)]; Available online: http://www.protezionecivile.gov.it/riskactivities/health-risk/emergencie....
-
- Ministero della Salute COVID-19 Situazione in Italia. Report 18–24 maggio. [(accessed on 20 May 2020)]; Available online: http://www.salute.gov.it/portale/nuovocoronavirus/dettaglioContenutiNuov....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

