Direct cortical thickness estimation using deep learning-based anatomy segmentation and cortex parcellation
- PMID: 32786059
- PMCID: PMC7643371
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25159
Direct cortical thickness estimation using deep learning-based anatomy segmentation and cortex parcellation
Abstract
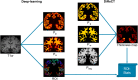
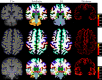
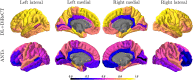
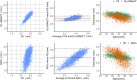
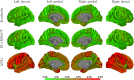
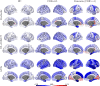
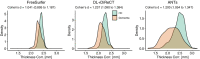
Accurate and reliable measures of cortical thickness from magnetic resonance imaging are an important biomarker to study neurodegenerative and neurological disorders. Diffeomorphic registration-based cortical thickness (DiReCT) is a known technique to derive such measures from non-surface-based volumetric tissue maps. ANTs provides an open-source method for estimating cortical thickness, derived by applying DiReCT to an atlas-based segmentation. In this paper, we propose DL+DiReCT, a method using high-quality deep learning-based neuroanatomy segmentations followed by DiReCT, yielding accurate and reliable cortical thickness measures in a short time. We evaluate the methods on two independent datasets and compare the results against surface-based measures from FreeSurfer. Good correlation of DL+DiReCT with FreeSurfer was observed (r = .887) for global mean cortical thickness compared to ANTs versus FreeSurfer (r = .608). Experiments suggest that both DiReCT-based methods had higher sensitivity to changes in cortical thickness than Freesurfer. However, while ANTs showed low scan-rescan robustness, DL+DiReCT showed similar robustness to Freesurfer. Effect-sizes for group-wise differences of healthy controls compared to individuals with dementia were highest with the deep learning-based segmentation. DL+DiReCT is a promising combination of a deep learning-based method with a traditional registration technique to detect subtle changes in cortical thickness.
Keywords: MRI; brain morphometry; cortical thickness; deep learning; diffeomorphic registration; gray matter atrophy; neuroanatomy segmentation.
© 2020 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
References
-
- Buckner, R. L. , Head, D. , Parker, J. , Fotenos, A. F. , Marcus, D. , Morris, J. C. , & Snyder, A. Z. (2004). A unified approach for morphometric and functional data analysis in young, old, and demented adults using automated atlas‐based head size normalization: Reliability and validation against manual measurement of total intracranial volume. NeuroImage, 23(2), 724–738. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.06.018 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG043434/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH056584/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB009352/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021910/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- CRSII5_180365/SNSF_/Swiss National Science Foundation/Switzerland
- P50 MH071616/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR021382/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

