Discovery of First-in-Class Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) Degraders
- PMID: 32787082
- PMCID: PMC7486226
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01111
Discovery of First-in-Class Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) Degraders
Abstract
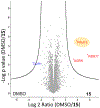
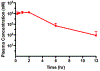
The aberrant expression of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) has been associated with multiple cancers. Using the proteolysis targeting chimera technology, we discovered a first-in-class PRMT5 degrader 15 (MS4322). Here, we report the design, synthesis, and characterization of compound 15 and two structurally similar controls 17 (MS4370) and 21 (MS4369), with impaired binding to the von Hippel-Lindau E3 ligase and PRMT5, respectively. Compound 15, but not 17 and 21, effectively reduced the PRMT5 protein level in MCF-7 cells. Our mechanism studies indicate that compound 15 degraded PRMT5 in an E3 ligase- and proteasome-dependent manner. Compound 15 also effectively reduced the PRMT5 protein level and inhibited growth in multiple cancer cell lines. Moreover, compound 15 was highly selective for PRMT5 in a global proteomic study and exhibited good plasma exposure in mice. Collectively, compound 15 and its two controls 17 and 21 are valuable chemical tools for exploring the PRMT5 functions in health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
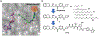

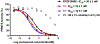

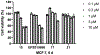

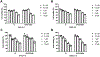


References
-
- Branscombe TL; Frankel A; Lee J-H; Cook JR; Yang Z.-h.; Pestka S; Clarke S. PRMT5 (Janus kinase-binding protein 1) catalyzes the formation of symmetric dimethylarginine residues in proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32971−32976. - PubMed
-
- Migliori V; Müller J; Phalke S; Low D; Bezzi M; Mok WC; Sahu SK; Gunaratne J; Capasso P; Bassi C; Cecatiello V; De Marco A; Blackstock W; Kuznetsov V; Amati B; Mapelli M; Guccione E. Symmetric dimethylation of H3R2 is a newly identified histone mark that supports euchromatin maintenance. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 136−144. - PubMed
-
- Musiani D; Bok J; Massignani E; Wu L; Tabaglio T; Ippolito MR; Cuomo A; Ozbek U; Zorgati H; Ghoshdastider U; Robinson RC; Guccione E; Bonaldi T Proteomics profiling of arginine methylation defines PRMT5 substrate specificity. Sci. Signaling 2019, 12, No. eaat8388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

