Dynamic changes of throat swabs RNA and serum antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 and their diagnostic performances in patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 32787527
- PMCID: PMC7534196
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1810133
Dynamic changes of throat swabs RNA and serum antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 and their diagnostic performances in patients with COVID-19
Abstract
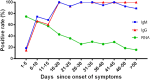
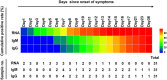
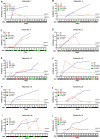
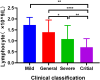
Dynamic changes of RNA and antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients remain largely unknown, and influence factors for antibody production have not been fully clarified. In this study, consecutive throat swabs specimens (n = 1875) from 187 patients were collected to analyse the dynamic changes of RNA. Moreover, 162 serial serum samples from 31 patients were tested for seroconversion of IgM and IgG. Meanwhile, IgM and IgG were also detected in 409 COVID-19 patients and 389 controls. Additionally, the logistic regression analysis was executed to identify the possible influence factors for antibody production. The median positive conversion time for RNA was day 7 (IQR, 3-11), and the positive rate was highest in day 1-5 (74.59 %) and then gradually decreased. The median time of seroconversion for IgM and IgG were both day 12 (IQR, 10-15). The sensitivity and specificity for IgM (or IgG) was 87.04% and 96.92%, respectively. Multivariate logistic regression indicated that reduced lymphocytes and short positive conversion time for SARS-CoV-2 RNA were independent factors for negative results of IgM and IgG. In conclusion, RNA and antibodies should be combined for COVID-19 diagnosis, and delayed seroconversion was influenced by the decreased lymphocytes and short positive conversion time for RNA.
Keywords: Antibody; COVID-19; RNA; SARS-CoV-2; throat swabs.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG Seropositivity to Detect COVID-19.J Appl Lab Med. 2020 Sep 1;5(5):908-920. doi: 10.1093/jalm/jfaa079. J Appl Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32428207 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody Detection and Dynamic Characteristics in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019.Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Nov 5;71(8):1930-1934. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa461. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32306047 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of performance of two SARS-CoV-2 Rapid IgM-IgG combined antibody tests on capillary whole blood samples from the fingertip.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 17;15(9):e0237694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237694. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32941461 Free PMC article.
-
[SARS-CoV-2 and Microbiological Diagnostic Dynamics in COVID-19 Pandemic].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020 Jul;54(3):497-509. doi: 10.5578/mb.69839. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020. PMID: 32755524 Review. Turkish.
-
Value and Validity of Coronavirus Antibody Testing.Pain Physician. 2020 Aug;23(4S):S381-S390. Pain Physician. 2020. PMID: 32942795 Review.
Cited by
-
High Performance of SARS-Cov-2N Protein Antigen Chemiluminescence Immunoassay as Frontline Testing for Acute Phase COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 14;8:676560. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.676560. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34336884 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical applications of detecting IgG, IgM or IgA antibody for the diagnosis of COVID-19: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Mar;104:415-422. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.01.016. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33450372 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-8 as a Biomarker for Disease Prognosis of Coronavirus Disease-2019 Patients.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 8;11:602395. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.602395. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33488599 Free PMC article.
-
Immune response to and virological profile of SARS-CoV-2 before and after symptom onset in individuals vaccinated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccines.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2518654. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2518654. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40530661 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to the editor: Multiple large preretinal hemorrhages in the context of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection.Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2021 Nov-Dec;84(6):628-629. doi: 10.5935/0004-2749.20210123. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2021. PMID: 34817031 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO . Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Situation Report-108 [7 May 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio....
-
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China . The Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (7th version): National Health Commission of China; [7 May 2020]. Available from: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb19....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
