Comprehensive review of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- PMID: 32788071
- PMCID: PMC7263230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.05.023
Comprehensive review of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Abstract
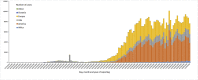
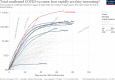
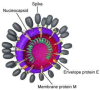
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was first identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, the capital of China's Hubei province and has rapidly spread all over the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak to be a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 01/30/2020 and recognized it as a pandemic on 03/11/2020. The number of people diagnosed with COVID-19 worldwide crossed the one million mark on 04/02/2020; two million mark on 04/15/2020; three million mark on 04/27/2020 and the four million mark on 05/09/2020. Despite containment efforts, more than 187 countries have been affected with more than 4,178,346 cases in the world with maximum being in USA (1,347,936) followed by 227,436 in Spain and 224,422 in United Kingdom as of May, 2020. COVID-19 is the latest threat to face mankind cutting across geographical barriers in a rapidly changing landscape. This review provides an update on a rapidly evolving global pandemic. As we face the threat of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases, this is a stark reminder to invest in population health, climate change countermeasures, a global health surveillance system and effective research into identifying pathogens, their treatment and prevention and effective health delivery systems.
Keywords: COVID-19; Global health emergency; Novel coronavirus; Pandemic; SARS CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Chang Gung University. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- GISAID database. 2020 coronavirus. J Med Virol. April 2020
-
- WHO.int. Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations . World Health Organization; 2005. Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-.... [Accessed 25 March 2020]
-
- WHO.int WHO Summary of probable SARS cases with onset of illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003
-
- WHO. int. Europe Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous