Portal Vein Stenosis Following Liver Transplantation Hemodynamically Assessed with 4D-flow MRI before and after Portal Vein Stenting
- PMID: 32788504
- PMCID: PMC8424031
- DOI: 10.2463/mrms.ici.2020-0057
Portal Vein Stenosis Following Liver Transplantation Hemodynamically Assessed with 4D-flow MRI before and after Portal Vein Stenting
Abstract
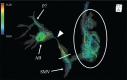
We present a case of a patient who underwent portal vein (PV) stenting for PV stenosis after a living-donor liver transplantation. A pretreatment 3D cine phase-contrast (4D-flow) MRI showed decreased, though hepatopetal, blood flow in the PV. After stenting, 4D-flow MRI confirmed an improvement in PV flow, with a more homogeneous flow distribution to each hepatic segment. 4D-flow MRI are valuable for understanding the hemodynamics of this area, planning for treatments, and evaluating the outcome of the interventions.
Keywords: 4D-flow MRI; living-donor liver transplantation; portal vein stenosis; portal vein stenting.
Conflict of interest statement
The second author Yasuo Takehara is an endowed chair of Nagoya University supported by a private company Himedic Nagoya; however, the status is irrelevant to the contents of this paper. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Craig EV, Heller MT. Complications of liver transplant. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2021; 46:43–67. - PubMed
-
- Cheng YF, Ou HY, Tsang LL, et al. Vascular stents in the management of portal venous complications in living donor liver transplantation. Am J Transplant 2010; 10:1276–1283. - PubMed
-
- Markl M, Chan FP, Alley MT, et al. Time-resolved three-dimensional phase-contrast MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2003; 17:499–506. - PubMed

