Contribution of the murI Gene Encoding Glutamate Racemase in the Motility and Virulence of Ralstonia solanacearum
- PMID: 32788894
- PMCID: PMC7403515
- DOI: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.03.2020.0049
Contribution of the murI Gene Encoding Glutamate Racemase in the Motility and Virulence of Ralstonia solanacearum
Abstract
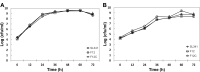
Bacterial traits for virulence of Ralstonia solanacearum causing lethal wilt in plants were extensively studied but are not yet fully understood. Other than the known virulence factors of Ralstonia solanacearum, this study aimed to identify the novel gene(s) contributing to bacterial virulence of R. solanacearum. Among the transposon-inserted mutants that were previously generated, we selected mutant SL341F12 strain produced exopolysaccharide equivalent to wild type strain but showed reduced virulence compared to wild type. In this mutant, a transposon was found to disrupt the murI gene encoding glutamate racemase which converts L-glutamate to D-glutamate. SL341F12 lost its motility, and its virulence in the tomato plant was markedly diminished compared to that of the wild type. The altered phenotypes of SL341F12 were restored by introducing a full-length murI gene. The expression of genes required for flagella assembly was significantly reduced in SL341F12 compared to that of the wild type or complemented strain, indicating that the loss of bacterial motility in the mutant was due to reduced flagella assembly. A dramatic reduction of the mutant population compared to its wild type was apparent in planta (i.e., root) than its wild type but not in soil and rhizosphere. This may contribute to the impaired virulence in the mutant strain. Accordingly, we concluded that murI in R. solanacearum may be involved in controlling flagella assembly and consequently, the mutation affects bacterial motility and virulence.
Keywords: bacterial wilt disease; glutamate racemase; tomato plant.
© The Korean Society of Plant Pathology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ralstonia solanacearum needs motility for invasive virulence on tomato.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jun;183(12):3597-605. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.12.3597-3605.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11371523 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of glutamate racemase (MurI) eliminates virulence in Streptococcus mutans.Microbiol Res. 2016 May-Jun;186-187:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2016.02.003. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Microbiol Res. 2016. PMID: 27242137
-
Identification and characterization of virulence-attenuated mutants in Ralstonia solanacearum as potential biocontrol agents against bacterial wilt of Pogostemon cablin.Microb Pathog. 2020 Oct;147:104418. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104418. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32739402
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Tomato Xylem Sap Fitness Factors for Three Plant-Pathogenic Ralstonia Species.mSystems. 2021 Dec 21;6(6):e0122921. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.01229-21. Epub 2021 Nov 2. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34726495 Free PMC article.
-
The involvement of the Type Six Secretion System (T6SS) in the virulence of Ralstonia solanacearum on brinjal.3 Biotech. 2020 Jul;10(7):324. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02311-4. Epub 2020 Jun 29. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 32656057 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Screening and Identification of Natural Compounds as Potential Inhibitors of Glutamate Racemase, an Emerging Drug Target of Food Pathogen E. coli O157:H7: An In-silico Approach to Combat Increasing Drug Resistance.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2025;25(2):e18715265306131. doi: 10.2174/0118715265306131240809095241. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39161148
-
Comprehensive genome sequence analysis of Ralstonia solanacearum gd-2, a phylotype I sequevar 15 strain collected from a tobacco bacterial phytopathogen.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 14;15:1335081. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1335081. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38550868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayot R. G., Ries S. M. Role of motility in apple blossom infection by Erwinia amylovora and studies of fire blight control with attractant and repellent compounds. Phytopathology. 1986;76:441–445. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-76-441. - DOI
-
- Boucher C. A., Barberis P. A., Trigalet A., Demery D. A. Transposon mutagenesis of Pseudomonas solanacearum: isolation of Tn5-induced avirulent mutants. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1985;131:2449–2457. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2449. - DOI
-
- Chuaboon W., Athinuwat D., Kaewnum S., Burr T. J., Prathuangwong S. Genes associated with production of flagella and a pectate lyase affect virulence and associated activities in Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. glycines. Thai J. Agric. Sci. 2014;47:115–132.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

