Lung Insufflation Capacity with a New Device in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Measurement of the Lung Volume Recruitment in Respiratory Therapy
- PMID: 32789279
- PMCID: PMC7365237
- DOI: 10.2490/prm.20200011
Lung Insufflation Capacity with a New Device in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Measurement of the Lung Volume Recruitment in Respiratory Therapy
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to validate the usefulness of the measurement of lung insufflation capacity (LIC) using the LIC TRAINER (LT) in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
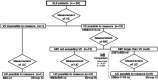
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted in the rehabilitation departments of the Japanese National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry and involved 20 ALS patients who underwent respiratory therapy between April 1, 2014, and December 2017. The vital capacity (VC), maximum insufflation capacity (MIC), and LIC measurements at the start of respiratory therapy were extracted from the medical records, and patients were divided into three groups: group A, VC could not be measured; group B, VC could be measured, but MIC was less than VC; and group C, MIC was larger than VC. LIC could be measured in all groups. In group C, paired t-tests were used to analyze whether there was a significant difference in the volumes measured using different methods.
Results: LIC was 950, 1863±595, and 2980±1176 ml in groups A (n=1), B (n=10), and C (n=9), respectively. In groups A and B, LIC could be measured in all patients, even when VC or MIC could not be measured. In group C, the measured LIC value was significantly greater than MIC (p=0.003).
Conclusion: LIC could be successfully measured using the LT. By using the LT, it was feasible to conveniently perform LIC measurements, suggesting that it could be a useful device for performing respiratory therapy in ALS patients.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; lung insufflation capacity; lung volume recruitment; new device; respiratory therapy.
©2020 The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: The LT was co-developed by our hospital and Cater Technologies (Saitama, Japan). The authors state that they have no other conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chatwin M,Toussaint M,Gonçalves MR,Sheers N,Mellies U,Gonzales-Bermejo J,Sancho J,Fauroux B,Andersen T,Hov B,Nygren-Bonnier M,Lacombe M,Pernet K,Kampelmacher M,Devaux C,Kinnett K,Sheehan D,Rao F,Villanova M,Berlowitz D,Morrow BM: Airway clearance techniques in neuromuscular disorders: a state of the art review. Respir Med 2018;136:98–110. 10.1016/j.rmed.2018.01.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Finder JD,Birnkrant D,Carl J,Farber HJ,Gozal D,Iannaccone ST,Kovesi T,Kravitz RM,Panitch H,Schramm C,Schroth M,Sharma G,Sievers L,Silvestri JM,Sterni L, American Thoracic Society: Respiratory care of the patient with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: ATS consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004;170:456–465. 10.1164/rccm.200307-885ST - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

