Functional connectivity within glioblastoma impacts overall survival
- PMID: 32789494
- PMCID: PMC7992880
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa189
Functional connectivity within glioblastoma impacts overall survival
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma (GBM; World Health Organization grade IV) assumes a variable appearance on MRI owing to heterogeneous proliferation and infiltration of its cells. As a result, the neurovascular units responsible for functional connectivity (FC) may exist within gross tumor boundaries, albeit with altered magnitude. Therefore, we hypothesize that the strength of FC within GBMs is predictive of overall survival.
Methods: We used predefined FC regions of interest (ROIs) in de novo GBM patients to characterize the presence of within-tumor FC observable via resting-state functional MRI and its relationship to survival outcomes.
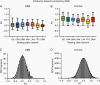
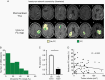
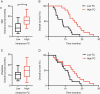
Results: Fifty-seven GBM patients (mean age, 57.8 ± 13.9 y) were analyzed. Functionally connected voxels, not identifiable on conventional structural images, can be routinely found within the tumor mass and was not significantly correlated to tumor size. In patients with known survival times (n = 31), higher intranetwork FC strength within GBM tumors was associated with better overall survival even after accounting for clinical and demographic covariates.
Conclusions: These findings suggest the possibility that functionally intact regions may persist within GBMs and that the extent to which FC is maintained may carry prognostic value and inform treatment planning.
Keywords: FC; functional MRI; glioblastoma; glioma; resting state.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology.
Figures

References
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(5):492–507. - PubMed
-
- Ojemann JG, Miller JW, Silbergeld DL. Preserved function in brain invaded by tumor. Neurosurgery. 1996;39(2):253–25 8; discussion 258. - PubMed
-
- Skirboll SS, Ojemann GA, Berger MS, Lettich E, Winn HR. Functional cortex and subcortical white matter located within gliomas. Neurosurgery. 1996;38(4):678–6 84; discussion 684. - PubMed
-
- Schiffbauer H, Ferrari P, Rowley HA, Berger MS, Roberts TP. Functional activity within brain tumors: a magnetic source imaging study. Neurosurgery. 2001;49(6):1313–13 20; discussion 1320. - PubMed

