Evaluation of belimumab treatment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in a clinical practice setting: Results from a 24-month OBSErve study in Argentina
- PMID: 32791930
- PMCID: PMC7536527
- DOI: 10.1177/0961203320947814
Evaluation of belimumab treatment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in a clinical practice setting: Results from a 24-month OBSErve study in Argentina
Abstract
Objective: To describe clinical effectiveness of belimumab for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in real-world practice in Argentina.
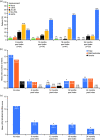
Methods: This retrospective, observational study analysed medical record data of patients with SLE treated with belimumab in 15 centres in Argentina. Primary endpoint: overall clinical response (assessed on a scale similar to the 6-point Physician Global Assessment) at months 6, 12, 18 and 24, all versus index (belimumab initiation). Secondary endpoints: improvement in disease activity (SELENA-SLEDAI), SLE manifestations, and corticosteroid dose change.
Results: Records for 81 patients (91% female) were analysed. Clinical improvements were reported for 95%, 95%, 98% and 100% patients at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months post index, respectively. Mean SELENA-SLEDAI score decreased from 11.21 at index to 4.76, 3.77, 3.86 and 2.17 at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months post index, respectively. Number of flares decreased from 1.05 at index to 0.21, 0.09, 0.22 and 0.30 at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months post index, respectively. Mean corticosteroid dose was 14.59 mg/day at index, and 6.45, 5.18, 5.17 and 4.78 mg/day at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months post index, respectively.
Conclusions: Real-world patients with SLE treated with belimumab in Argentina demonstrated clinical improvements and reductions in corticosteroid dose.
Keywords: Belimumab; disease activity; observational study; real-world; steroid sparing; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures



References
-
- Scolnik M, Soriano ER. Epidemiology of lupus in Latin America. Lupus Open Access 2016; 01: 110.
-
- Danchenko N, Satia JA, Anthony MS. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of worldwide disease burden. Lupus 2006; 15: 308–318. - PubMed
-
- Bertsias G, Ioannidis JP, Boletis J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Report of a task force of the EULAR standing committee for international clinical studies including therapeutics. Ann Rheum Dis 2008; 67: 195–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

