Comparative analgesic efficacy of intravenous vs intrathecal dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to hyperbaric bupivacaine in subarachnoid block for below knee orthopaedic surgery
- PMID: 32792709
- PMCID: PMC7398016
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_219_20
Comparative analgesic efficacy of intravenous vs intrathecal dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to hyperbaric bupivacaine in subarachnoid block for below knee orthopaedic surgery
Abstract
Background and aim: Intrathecal and intravenous dexmedetomidine has been used as adjuvant in subarachnoid block [SAB]. The aim of this study was to compare the analgesic efficacy of intravenous vs intrathecal dexmedetomidine as adjuvant to intrathecal bupivacaine.
Methods: Ninety patients, aged 20-60 years belonging to American Society of Anaesthesiologists (ASA) physical status I and II, scheduled for below knee orthopaedic surgeries under SAB were enrolled. In group I (n = 45) patients received intravenous dexmedetomidine 0.5 μg/kg in 100 mL 0.9% normal saline [NS] intravenous over a period of 15 minutes given 20 minutes before SAB. Subarachnoid block was given with intrathecal (IT) 0.5% bupivacaine (H) 12.5 mg (2.5 mL) with 0.3 mL of NS. Patients in group II (n = 45) received 100 mL of 0.9% NS over a period of 15 minutes given 20 minutes before subarachnoid block. SAB was given with intrathecal 0.5% heavy bupivacaine 12.5 mg with 3 μg of dexmedetomidine (0.3 mL). The primary outcome was duration of analgesia and rescue analgesic requirement, whereas secondary outcome included pain scores.
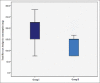
Results: The duration of analgesia was prolonged in group II (median [IQR]: 5 (6-7.5) h than in group I (median[IQR]: 4[2-4.5] h, P = 0.000). Median dose of rescue analgesics over period of 24 hours was less in group II as compared to group I (median [IQR]:150 (75-150) mg vs 195 (150-225) mg, P = 0.000). VAS score was lower in group II till 12 h in the postoperative period (P = 0.00).
Conclusion: Intrathecal dexmedetomidine is more efficacious as compared to intravenous dexmedetomidine, due to favourable outcomes in terms of increased duration of postoperative analgesia and reduced rescue analgesic requirement.
Keywords: Adjuvant; analgesia; dexmedetomidine; subarachnoid block.
Copyright: © 2020 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mauermann WJ, Shilling AM, Zuo Z. A comparison of neuraxial block versus general anesthesia for elective total hip replacement: A meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 2006;103:1018–25. - PubMed
-
- Hurley RW, Wu CL. Acute postoperative pain. In: Miller RD, editor. Miller's Anesthesia. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2010. pp. 2757–82.
-
- Ture P, Ramaswamy AH, Shaikh SI, Alur JB, Ture AV. Comparative evaluation of anaesthetic efficacy and haemodynamic effects of a combination of isobaric bupivacaine with buprenorphine vs. isobaric levobupivacaine with buprenorphine for spinal anaesthesia – A double blinded randomised clinical trial. Indian J Anaesth. 2019;63:49–54. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Solanki SL, Bharti NA, Batra YK, Jain A, Kumar P, Nikhar S. The analgesic effect of intrathecal dexmedetomidine or clonidine, with bupivacaine, in trauma patients undergoing lower limb surgery: A randomised, double-blind study. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2013;41:51–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
