Measurement of non-invasive blood pressure in lateral decubitus position under general anaesthesia - Which arm gives more accurate BP in relation to invasive BP - dependent or non-dependent arm?
- PMID: 32792741
- PMCID: PMC7413357
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_125_20
Measurement of non-invasive blood pressure in lateral decubitus position under general anaesthesia - Which arm gives more accurate BP in relation to invasive BP - dependent or non-dependent arm?
Abstract
Background and aims: Non-invasive blood pressure (NiBP) varies with the arm and body position. In the lateral decubitus position (LDP), the non-dependent arm reads lower, and the dependent arm reads higher pressure. We aimed to study the correlation between the NiBP and invasive arterial blood pressure (ABP) as anaesthesia progressed and its correlation in different BP ranges.
Methods: American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA I-III) patients, between 18-70 years undergoing neurosurgical procedures in the LDP were studied. All were anaesthetised using a standard protocol, positioned in the LDP. NiBP was measured every 15 min in both dependent and non-dependent arms and correlated with the ABP.
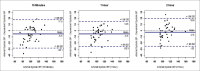
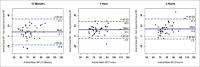
Results: Intra-class correlation (ICC) done between the dependent arm NiBP and ABP showed good correlation for mean and systolic BP and moderate correlation for diastolic BP. ICC was 0.800, 0.846 and 0.818 for mean and 0.771, 0.782, 0.792 for systolic BP at 15 min, 1 h, and 2 h, respectively. The ICC between the non-dependent arm NiBP and the invasive ABP showed poor correlation for all BP (systolic, diastolic and mean). As anaesthesia progressed, the mean difference between the NiBP and the ABP decreased in the dependent arm and increased in the non-dependent arm. The strength of agreement between the NiBP and the ABP in various BP ranges showed moderate correlation for the dependent arm NiBP (0.45-0.54) and poor correlation (0.21-0.38) for the non-dependent arm.
Conclusion: The NiBP of the dependent arm correlated well with ABP in LDP under general anaesthesia (GA). It is better to defer measuring NiBP in the non-dependent arm as the correlation with ABP is poor.
Keywords: Dependent arm; general anaesthesia; invasive arterial blood pressure; non-invasive blood pressure; supine position.
Copyright: © 2020 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Checketts MR, Alladi R, Ferguson K, Gemmell L, Handy JM, Klein AA, et al. Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland. Recommendations for standards of monitoring during anaesthesia and recovery 2015: Association of anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland. Anaesthesia. 2016;7:85–93. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ward M, Langton JA. Blood pressure measurement. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain. 2007:7122–6.
-
- Netea RT, Lenders JWM, Smits P, Thien T. Both body and arm position significantly influence blood pressure measurement. J Hum Hypertens. 2003;17:459–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials