Sex Differences in CMV Replication and HIV Persistence During Suppressive ART
- PMID: 32793766
- PMCID: PMC7415302
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa289
Sex Differences in CMV Replication and HIV Persistence During Suppressive ART
Abstract
Background: The association between subclinical cytomegalovirus (CMV) replication and HIV persistence has not been investigated in cis-gender women with HIV.
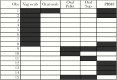
Methods: Fifty virologically suppressed female participants with HIV were prospectively enrolled and provided oral, vaginal, and urine samples and peripheral blood mononuclear cells at 1 cross-sectional time point. CMV DNA was quantified in each specimen by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Cellular HIV DNA and HIV RNA transcripts (unspliced and multiply spliced [ms] encoding tat-rev) were quantified by droplet digital (dd) PCR in peripheral blood cells. Forty-nine male individuals with HIV and CMV (historical data) were used as controls.
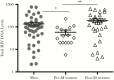
Results: Levels of cellular HIV DNA and unspliced HIV RNA were not different between sexes, but female participants had less detectable msHIV RNA and CMV DNA compared with males (both P < .01). Unlike previously described for males, the presence of CMV DNA was not associated with increased HIV DNA in females. Among female participants, premenopausal status was independently associated with lower HIV DNA compared with postmenopause, after adjusting for nadir CD4 count (P < .01).
Conclusions: Female participants with HIV had reduced cellular HIV RNA and less subclinical CMV DNA compared with males but overall similar HIV DNA levels in our study. Postmenopausal status was independently associated with higher HIV DNA levels among female participants.
Keywords: CMV; HIV; sex differences.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Deeks SG, Verdin E, McCune JM. Immunosenescence and HIV. Curr Opin Immunol 2012; 24:501–6. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- K24 AI100665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA041007/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AG044325/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI118422/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DA034978/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI134295/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107345/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI147821/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD094646/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 DA051915/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI120009/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI131385/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DA041007/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI106039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

