This is a preprint.
IFN- γ and TNF- α drive a CXCL10 + CCL2 + macrophage phenotype expanded in severe COVID-19 and other diseases with tissue inflammation
- PMID: 32793902
- PMCID: PMC7418716
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.08.05.238360
IFN- γ and TNF- α drive a CXCL10 + CCL2 + macrophage phenotype expanded in severe COVID-19 and other diseases with tissue inflammation
Update in
-
IFN-γ and TNF-α drive a CXCL10+ CCL2+ macrophage phenotype expanded in severe COVID-19 lungs and inflammatory diseases with tissue inflammation.Genome Med. 2021 Apr 20;13(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00881-3. Genome Med. 2021. PMID: 33879239 Free PMC article.
Abstract
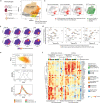
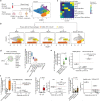
Immunosuppressive and anti-cytokine treatment may have a protective effect for patients with COVID-19. Understanding the immune cell states shared between COVID-19 and other inflammatory diseases with established therapies may help nominate immunomodulatory therapies. Using an integrative strategy, we built a reference by meta-analyzing > 300,000 immune cells from COVID-19 and 5 inflammatory diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Crohn's disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC), lupus, and interstitial lung disease. Our cross-disease analysis revealed that an FCN1 + inflammatory macrophage state is common to COVID-19 bronchoalveolar lavage samples, RA synovium, CD ileum, and UC colon. We also observed that a CXCL10 + CCL2 + inflammatory macrophage state is abundant in severe COVID-19, inflamed CD and RA, and expresses inflammatory genes such as GBP1, STAT1 , and IL1B . We found that the CXCL10 + CCL2 + macrophages are transcriptionally similar to blood-derived macrophages stimulated with TNF- α and IFN- γ ex vivo . Our findings suggest that IFN- γ , alongside TNF- α , might be a key driver of this abundant inflammatory macrophage phenotype in severe COVID-19 and other inflammatory diseases, which may be targeted by existing immunomodulatory therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
