WEARCON: wearable home monitoring in children with asthma reveals a strong association with hospital based assessment of asthma control
- PMID: 32795352
- PMCID: PMC7427745
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-020-01210-1
WEARCON: wearable home monitoring in children with asthma reveals a strong association with hospital based assessment of asthma control
Abstract
Background: Asthma is one of the most common chronic diseases in childhood. Regular follow-up of physiological parameters in the home setting, in relation to asthma symptoms, can provide complementary quantitative insights into the dynamics of the asthma status. Despite considerable interest in asthma home-monitoring in children, there is a paucity of scientific evidence, especially on multi-parameter monitoring approaches. Therefore, the aim of this study is to investigate whether asthma control can be accurately assessed in the home situation by combining parameters from respiratory physiology sensors.
Methods: Sixty asthmatic and thirty non-asthmatic children were enrolled in the observational WEARCON-study. Asthma control was assessed according to GINA guidelines by the paediatrician. All children were also evaluated during a 2-week home-monitoring period with wearable devices; a physical activity tracker, a handheld spirometer, smart inhalers, and an ambulatory electrocardiography device to monitor heart and respiratory rate. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to determine which diagnostic measures were associated with asthma control.
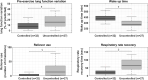
Results: 24 of the 27 uncontrolled asthmatic children and 29 of the 32 controlled asthmatic children could be accurately identified with this model. The final model showed that a larger variation in pre-exercise lung function (OR = 1.34 95%-CI 1.07-1.68), an earlier wake-up-time (OR = 1.05 95%-CI 1.01-1.10), more reliever use (OR = 1.11 95%-CI 1.03-1.19) and a longer respiratory rate recovery time (OR = 1.12 95%-CI 1.05-1.20) were significant contributors to the probability of having uncontrolled asthma.
Conclusions: Home-monitoring of physiological parameters correlates with paediatrician assessed asthma control. The constructed multivariate model identifies 88.9% of all uncontrolled asthmatic children, indicating a high potential for monitoring of asthma control. This may allow healthcare professionals to assess asthma control at home.
Trial registration: Netherlands Trail Register, NL6087 . Registered 14 February 2017.
Keywords: Ambulatory monitoring; Asthma control; Inhaler use; Multivariate analysis; Paediatrics; Physiology sensors; Telemedicine; Wearable electronic devices; eHealth; spirometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Wijga AH, Kerkhof M, Gehring U, de Jongste JC, Postma DS, Aalberse RC, et al. Cohort profile: The Prevention and Incidence of Asthma and Mite Allergy (PIAMA) birth cohort. Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43(2):527–535. - PubMed
-
- Merikallio VJ, Mustalahti K, Remes ST, Valovirta EJ, Kaila M. Comparison of quality of life between asthmatic and healthy school children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2005;16(4):332–340. - PubMed
-
- Long Alliantie Nederland . Zorgstandaard astma Kinderen & Jongeren. 2012. pp. 1–119.
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma . Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2019.

