Oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism (rs53576) and digit ratio associates with aggression: comparison in seven ethnic groups
- PMID: 32795360
- PMCID: PMC7427763
- DOI: 10.1186/s40101-020-00232-y
Oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism (rs53576) and digit ratio associates with aggression: comparison in seven ethnic groups
Abstract
Background: The specific role of the oxytocin receptor (OXTR) gene polymorphisms in emotional support seeking, related to social norms and culturally normative behavior, has been discussed in several studies. Evidence on the association between aggression and OXTR polymorphisms has also been reported. The goal of the current study was to analyze the effect of the OXTR rs53576 polymorphism, prenatal testosterone effect (second-to-fourth digit ratio, or 2D:4D), and culture on aggression assessed with the Buss-Perry Aggression Questionnaire (BPAQ).
Methods: The data were collected in Russia and Tanzania and included seven ethnic groups of European, Asian, and African origin. The total sample included 1705 adults (837 males, 868 females). All the subjects were evaluated with the BPAQ. As a measure of prenatal androgenization, the second and fourth digits were measured directly from hand, and the digit ratios were calculated. All the participants provided buccal samples, from which genomic DNA was extracted, and the OXTR gene rs53576 polymorphism was genotyped. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 23.0; the alpha level for all analyses was set at 0.05.
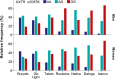
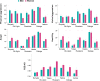
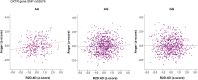
Results: The ethnic group factor was the most significant predictor of ratings on BPAQ (medium effect size for physical aggression, anger and hostility scales, and low for verbal aggression). To study the effect of sex, the OXTR polymorphism, and prenatal androgenization, we conducted the z-score transformation for BPAQ scales and 2D:4D for each ethnic group and pooled these data into new z-score variables. According to the GLM analysis after leveling the effects of culture (z-transformation), all four scales of BPAQ demonstrated association with sex (main effects), with men scoring higher on physical and verbal aggression and women scoring higher on anger and hostility. Anger and hostility scales were also associated with OXTR polymorphism and 2D:4D of the right hand. The lowest levels of anger and hostility were observed in individuals with the AA genotype, especially in men.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that both oxytocin (OXTR gene polymorphism) and fetal testosterone (2D:4D) may significantly affect emotional (anger) and cognitive (hostility) aggression in humans, given the leveling the role of culture.
Keywords: 2D:4D; Africans; Asians; Buss-Perry Aggression Questionnaire; Digit ratio; Ethnic groups; Europeans; Men; OXTR rs53576; Women.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The association between 2D:4D ratio and cognitive empathy is contingent on a common polymorphism in the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR rs53576).Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015 Aug;58:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.04.007. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25935637
-
Effect of the interaction between oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism (rs53576) and stressful life events on aggression in Chinese Han adolescents.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Oct;96:35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29890447
-
Evaluation of the Relationship Between Aggression and Digit Ratio Through a Cross-Sectional Study Among Hitit University Students.Am J Hum Biol. 2025 Jul;37(7):e70098. doi: 10.1002/ajhb.70098. Am J Hum Biol. 2025. PMID: 40579991
-
Is the Second to Fourth Digit Ratio (2D:4D) a Biomarker of Sex-Steroids Activity?Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2017 Jun;14(4):378-386. doi: 10.17458/per.vol14.2017.SSE.SexSteroids. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28613048 Review.
-
The oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) is associated with autism spectrum disorder: a meta-analysis.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 May;20(5):640-6. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.77. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25092245 Review.
Cited by
-
Childhood Trauma and Aggression in Persons Convicted for Homicide: An Exploratory Study Examines the Role of Plasma Oxytocin.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Aug 17;12:719282. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.719282. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34484006 Free PMC article.
-
Trends of Anger and Physical Aggression in Russian Women During COVID-19 Lockdown.Front Glob Womens Health. 2021 Oct 20;2:698151. doi: 10.3389/fgwh.2021.698151. eCollection 2021. Front Glob Womens Health. 2021. PMID: 34816235 Free PMC article.
-
Recalled Parental Bonding Interacts with Oxytocin Receptor Gene Polymorphism in Modulating Anxiety and Avoidance in Adult Relationships.Brain Sci. 2021 Apr 14;11(4):496. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11040496. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919740 Free PMC article.
-
The association between 2D:4D digit ratio and sex-typed play in children with and without siblings.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 2;14(1):15231. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65739-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38956189 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional biomarkers of the insula subregions predict sex differences in aggression subscales.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Jun 15;43(9):2923-2935. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25826. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 35289969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyd R, Richerson PJ. Culture and the evolutionary process. Chicago: University of Chicago press; 1988.
-
- Carter CS, Cushing BS. Proximate mechanisms regulating sociality and social monogamy, in the context of evolution. In: Chapman AR, Sussman RW, editors. The origins and nature of sociality. New York: Aldine de Gruyter; 2017. p. 99–121.
-
- House BR. How do social norms influence prosocial development? Curr Opin Psychol. 2018;20:87–91. - PubMed
-
- Fehr E, Gächter S. Altruistic punishment in humans. Nature. 2002;415(6868):137–140. - PubMed
-
- Boyd R. A different kind of animal: how culture transformed our species. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2017.

