Structure of phospholipase Cε reveals an integrated RA1 domain and previously unidentified regulatory elements
- PMID: 32796910
- PMCID: PMC7427993
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-01178-8
Structure of phospholipase Cε reveals an integrated RA1 domain and previously unidentified regulatory elements
Abstract
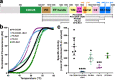
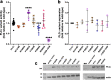
Phospholipase Cε (PLCε) generates lipid-derived second messengers at the plasma and perinuclear membranes in the cardiovascular system. It is activated in response to a wide variety of signals, such as those conveyed by Rap1A and Ras, through a mechanism that involves its C-terminal Ras association (RA) domains (RA1 and RA2). However, the complexity and size of PLCε has hindered its structural and functional analysis. Herein, we report the 2.7 Å crystal structure of the minimal fragment of PLCε that retains basal activity. This structure includes the RA1 domain, which forms extensive interactions with other core domains. A conserved amphipathic helix in the autoregulatory X-Y linker of PLCε is also revealed, which we show modulates activity in vitro and in cells. The studies provide the structural framework for the core of this critical cardiovascular enzyme that will allow for a better understanding of its regulation and roles in disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kadamur G, Ross EM. Mammalian phospholipase C. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013;75:127–54. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. The inositol trisphosphate/calcium signaling pathway in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016;96:1261–96. - PubMed
-
- Fukami, K., Inanobe, S., Kanemaru, K. & Nakamura, Y. Phospholipase C is a key enzyme regulating intracellular calcium and modulating the phosphoinositide balance. Prog. Lipid Res.49, 429–437 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

