Factors associated with HIV testing and intention to test for HIV among the general population of Nonthaburi Province, Thailand
- PMID: 32797048
- PMCID: PMC7428091
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237393
Factors associated with HIV testing and intention to test for HIV among the general population of Nonthaburi Province, Thailand
Abstract
Background: Research on HIV testing in Thailand has largely focused on at-risk population groups, with limited information about the prevalence of correlates of HIV testing among the Thai general population. This study addresses this gap in research by using a population-based probability sample to examine correlates of HIV testing experience and intention to test.
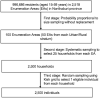
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional survey in Nonthaburi, Thailand during October-December 2012 using tablet computers to collect self-administered questionnaires from 2138 men and women (aged 15-59 years) identified through three-stage stratified cluster sampling.
Findings: Almost half of the respondents, 962 (45%), reported having been tested for HIV while an almost equal proportion, 1032 (48.3%), indicated their intention to test for HIV. Being sexually experienced, having a history of sexually transmitted infection, personally knowing someone infected with HIV, and youth were associated with both history of HIV testing and intention to test for HIV. High perceived risk of HIV, knowledge of an HIV testing location, and having been married were associated with having been tested for HIV. Having been tested for HIV and HIV/AIDS education were associated with intention to test for HIV. The most common reasons for testing were routine medical checkup and antenatal care. The major reasons for not testing were perception of having no or low risk.
Conclusion: A substantially low proportion of the respondents reported a history of HIV testing and intention to test for HIV. Culturally appropriate programs that address HIV risk perception and provide accurate information related to HIV infection and HIV testing may be beneficial in increasing uptake of HIV testing among the general population in Thailand.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
References
-
- UNAIDS. Communities at the Centre. Defending rights, breaking barriers, reachng people with HIV services. 2019.
-
- Techasrivichien T, Darawuttimaprakorn N, Punpuing S, Musumari PM, Lukhele BW, El-Saaidi C, et al. Changes in Sexual Behavior and Attitudes Across Generations and Gender Among a Population-Based Probability Sample From an Urbanizing Province in Thailand. Archives of sexual behavior. 2016;45(2):367–82. Epub 2014/11/19. 10.1007/s10508-014-0429-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tangmunkongvorakul A, Carmichael G, Banwell C, Seubsman SA, Sleigh A. Intimate relationships among adolescents in different social groups in northern Thailand. The Southeast Asian journal of tropical medicine and public health. 2010;41(6):1475–93. Epub 2011/02/19. . - PubMed
-
- Chamratrithirong AKS, Podhisita C, Isarabhakdi P, Sabalying M. National Sexual Behavior Survey of Thailand. Nakhon Pathom: Institute for Population and Social Research; 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous